Gate Valve Types: Rising vs. Non-Rising Stem

Table of Contents
ToggleRising vs. Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve Types
In this post, we will delve into the differences between rising stem and non-rising stem gate valve types, focusing on their unique features, benefits, and applications. Also, we will provide a helpful mermaid diagram for easy comparison, ensuring you have all the information you need to make the best possible decision for your projects.
As a seasoned engineering professional, you understand the importance of selecting the right gate valves for your industrial applications. Gate valves are widely used in various industries due to their excellent shutoff capabilities and low-pressure drop. They control the flow of liquid or gas by raising or lowering a gate, which moves perpendicular to the flow direction. There are two main gate valve types: rising stem gate valves and non-rising stem gate valves.
Understanding Gate Valve Types in Industrial Applications
Gate valves play a critical role in controlling the flow of liquids and gases in industrial settings. They are specifically designed to start or stop flow, rather than regulate it. Understanding the function and key components of gate valves is crucial for ensuring smooth and efficient operations in various industrial applications.
The Function of Gate Valves
Gate valves are designed to provide a straight-through, unobstructed path for the flow of fluids. When fully open, gate valves minimize pressure drop and allow for optimal fluid flow. Their ability to completely shut off flow makes them suitable for applications where a tight seal is necessary, especially in systems with high pressures and temperatures. In industrial settings, gate valve types are commonly used in pipelines, oil and gas processing facilities, chemical plants, and water treatment plants.
Key Components of a Gate Valve
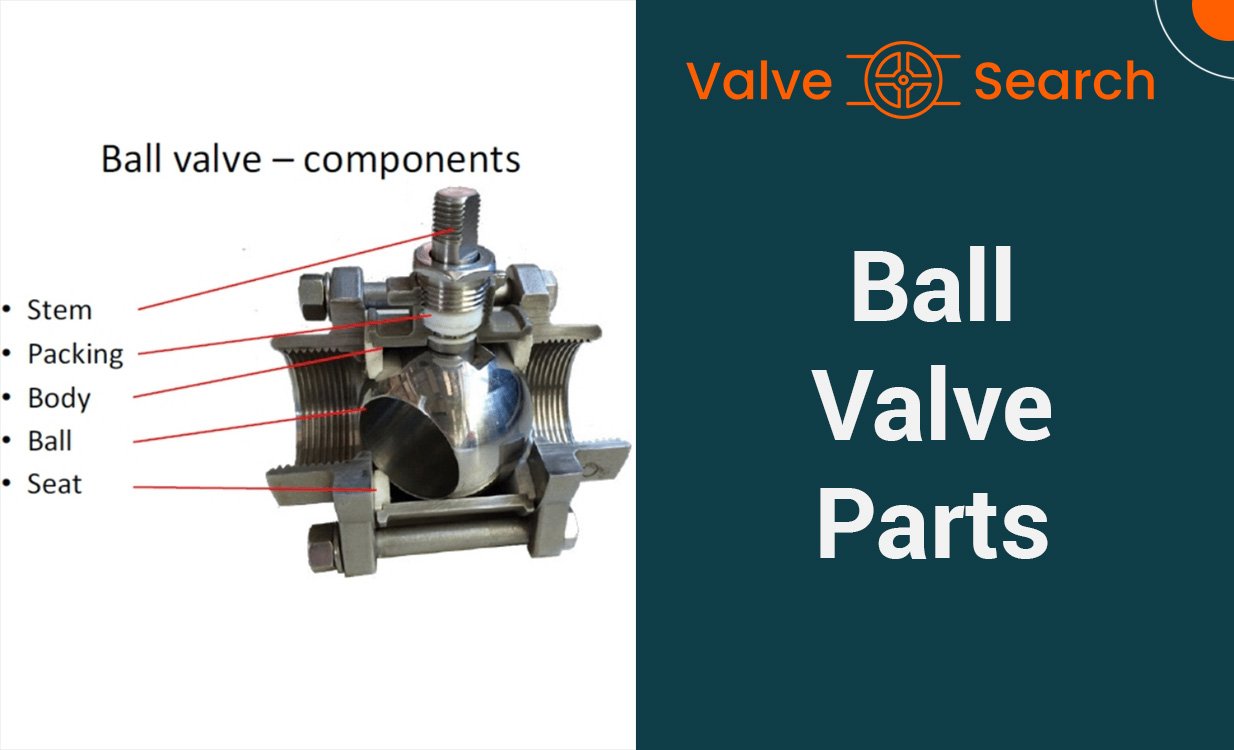
The key components of a gate valve include the body, bonnet, gate, stem, seat, and actuator. The body serves as the primary structure that contains and guides the flow of the fluid. The bonnet provides a cover for the valve’s internals and supports the valve stem. The gate, typically made of stainless steel or other durable materials, is the component that either stops or allows the flow of fluid. The stem connects the handwheel or actuator to the gate, enabling the opening and closing of the valve. The seat forms a tight seal with the gate to control the flow of the fluid, and the actuator, if present, automates the operation of the valve.
Understanding these key components is essential for selecting the right gate valve type for specific industrial applications, ensuring efficient performance, and minimizing the risk of operational issues.
The Basics of Stem Design in Gate Valve Types
Stem design is a crucial aspect of gate valves, impacting their reliability and performance. Understanding the function and construction of valve stems is essential for the proper operation of gate valves.
What is a Valve Stem?
The valve stem serves as a connection between the actuator and the gate inside the valve. When the actuator is engaged, the stem lowers or raises the gate to either block or permit the flow of fluid. In a gate valve, the stem is responsible for the linear motion of the gate, allowing precise control of the flow.
Stem Design and Valve Operation
The design of the valve stem directly influences the operation of the gate valve. Factors such as the material, length, and sealing mechanism of the stem impact the valve’s efficiency and longevity. A well-designed stem ensures smooth and reliable operation, while also minimizing the potential for leakage or damage.
Understanding the intricate relationship between stem design and valve operation is crucial for selecting the right gate valve for specific applications. The correct stem design contributes to the overall functionality and effectiveness of the gate valve, making it a critical consideration in industrial and commercial settings.
Rising Stem Gate Valves
Gate valves come in different types, and one of the varieties is the rising stem gate valve. These gate valve types have a stem that rises above the valve when the gate is opened. It is important to understand the structure, advantages, and applications of rising stem gate valves before using them in various industrial settings.
Structure of Rising Stem Gate Valves
Rising stem gate valves consist of a threaded stem that engages with the gate. As the handwheel is turned, the stem rises and lowers, allowing for easy visual confirmation of the valve’s position. This design makes it ideal for applications where the valve’s status needs to be clearly visible, such as in firefighting systems, water treatment plants, and high-pressure steam systems.
Advantages of Rising Stem Gate Valves
The design of rising stem gate valves allows for easy identification of whether the valve is open or closed without the need for additional monitoring equipment. This feature simplifies maintenance and operation, making it a cost-effective solution for many industrial applications. Additionally, the rising stem design minimizes the potential for water or other fluids to leak into the stem threads, reducing the risk of corrosion and ensuring smooth operation over time.
Applications Suited for Rising Stem Gate Valves
Rising stem gate valves are well-suited for applications where the visual indication of the valve position is critical. These may include water and wastewater treatment plants, power generation facilities, and firefighting systems. Their ability to provide a clear and immediate visual indication of the valve’s status makes them an optimal choice for critical systems where safety and reliability are paramount.
Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves
Structure of Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves
Non-rising stem gate valves are constructed with a stem that remains in a fixed position while the gate moves up and down along the threads of the stem. The gate is fixed onto the stem, and the nut travels along the threads of the stem to open and close the valve. This design makes non-rising stem gate valves more suitable for areas with limited space, as the elongation of the stem does not affect the valve’s operation.
Benefits of Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves
One of the key advantages of non-rising stem gate valves is their space-saving design, making them ideal for installations with height limitations. Additionally, the fixed position of the stem eliminates the need for a longer operating nut, resulting in a more compact valve structure. These gate valve types also reduce the risk of damage to the stem due to external factors, enhancing the valve’s durability and reliability.
Ideal Uses for Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves
Non-rising stem gate valves are commonly used in applications where space constraints are a concern, such as underground installations or areas with limited headroom. Their compact design also makes these gate valve types suitable for use in pipelines and systems where vertical space is restricted. Due to their construction, these gate valve types are often preferred in industrial settings, water treatment facilities, and irrigation systems where space efficiency is crucial.

Comparing Rising vs. Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve Types
The comparison between rising and non-rising stem gate valve types is essential for understanding their distinct features and applications in various industries. From visual differences and performance to maintenance considerations, these two gate valve types differ significantly, impacting their suitability for specific operational needs.
Visual Differences and Identification
Visually, rising stem gate valves feature a stem that extends or retracts as the valve is opened or closed, providing a clear indication of the valve’s position. In contrast, non-rising stem gate valves have a stem that remains in a fixed position regardless of the valve’s operation. This visual disparity between the two gate valve types allows for easy identification and differentiation during inspection and maintenance activities.
Performance Comparison of Two Gate Valve Types
In terms of performance, rising stem gate valves are well-suited for applications where start-stop functionality is crucial, as they completely remove the valve disc from the flow path when open, minimizing pressure drop. Non-rising stem gate valves, on the other hand, are ideal for environments where space constraints or limited installation height are primary considerations, as their design requires less vertical space.
Maintenance Considerations
Maintenance considerations for rising and non-rising stem gate valves vary based on their design complexities. Rising stem gate valves, with their exposed threading, facilitate easier lubrication, simplifying maintenance procedures. Conversely, non-rising stem gate valves may offer advantages in compact installations and environments where external stem movement could pose operational challenges, influencing the maintenance approach accordingly.
Selection Criteria for Gate Valve Types
When it comes to selecting the right type of gate valve for a specific application, several factors need to be taken into consideration. The selection process is critical to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and safety of the overall system. Below are the factors affecting valve type selection and industry recommendations for gate valve types.
Factors Affecting Valve Type Selection
- Nature of the Fluid: The nature of the fluid being handled is a primary factor in determining the type of gate valve required. Different gate valve types are designed to handle specific fluid properties such as viscosity, corrosiveness, and temperature.
- Operating Conditions: Understanding the operating conditions, including pressure and temperature ranges, is crucial. It ensures that the selected gate valve can withstand and operate effectively under the specific conditions it will be exposed to.
- Flow Requirements: The flow characteristics and flow control requirements of the system play a significant role in the selection of gate valves. It is essential to choose a valve type that can efficiently regulate the flow based on the system’s needs.
- System Compatibility: Compatibility with the existing system and components is essential to ensure seamless integration and functionality. The selected gate valve should align with the overall system design and requirements.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Considering the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the gate valve is vital for long-term cost-effectiveness. The valve should be accessible for maintenance and repairs as needed.
Industry Recommendations for Gate Valves
- Parallel Gate Valves: Recommended for applications requiring tight shut-off and reliable sealing, especially for slurries and abrasive media. The design features of parallel gate valves make them suitable for handling challenging fluid conditions.
- Knife Valves: Ideal for applications involving the shearing of entrained solids or separation of slurries, offering precise and efficient cut-off capabilities in such scenarios.
- Through-Conduit Gate Valves: Industry-recommended for applications where a full-area flow passageway and efficient shut-off are crucial. The design ensures uninterrupted flow and reliable sealing performance.
- Wedge-Shaped Gate Valves: These gate valve tyoes are suitable for handling non-condensing gases and liquids at normal temperatures, particularly corrosion-prone fluids. The split wedge design and inclined seats provide tight shut-off capabilities and flexibility.
In conclusion, the selection of gate valve types should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of the factors influencing the application’s requirements. Following industry recommendations ensures that the chosen gate valve type aligns with specific industry standards and performance expectations.
Installation and Safety Tips for Gate Valves
The installation of gate valves is a critical process that demands meticulous attention to safety measures to ensure smooth operation and protect the well-being of personnel. Adhering to essential precautions during the installation of gate valve types can help prevent accidents, injuries, and potential damage to the equipment.
Proper Installation Practices for Different Gate Valve Types
- Select Appropriate Valve Type and Size: Prior to installation, it is crucial to select the right valve type and size that matches the specific requirements of the fluid control system, considering factors such as pressure, temperature, and flow rate.
- Thorough Inspection: Before installation, conduct a comprehensive inspection of the valve components to identify any signs of damage or defects that may compromise its functionality.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for proper installation, ensuring that all necessary tools and equipment are readily available and in good working condition.
- Wear Personal Protective Equipment: Workers must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety goggles, and hard hats to minimize the risk of injuries during the installation process.
- Workspace Safety: Ensure that the workspace is clean, well-lit, and free of potential hazards like debris or slippery surfaces to minimize the risk of accidents.
- Conduct Pressure and Leak Tests: After installation, conduct pressure and leak tests to verify the performance and integrity of the gate valve.
- Secure the Valve: Properly secure the valve in place using suitable supports and anchoring methods to prevent accidental dislodging or movement, which could pose a significant risk to both personnel and equipment.
Safety Measures During Operation
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Conduct regular maintenance and inspections to identify and address any issues that may arise over time, ensuring the continued safe operation of the gate valve within the fluid control system.
- Training and Education: Provide proper training and education to personnel involved in the operation and maintenance of gate valves to ensure they are aware of safety protocols and procedures.
- Emergency Response Plan: Establish an effective emergency response plan to address any potential safety hazards or valve-related incidents promptly.
By following these installation and safety tips, you can achieve a successful gate valve installation while minimizing risks and creating a secure work environment for all involved parties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between rising stem gate valves and non-rising stem gate valves is crucial for selecting the right valve for your industrial applications. Rising stem gate valves offer the advantage of providing a clear visual indicator of the valve’s position, ensuring proper flow control and safety. On the other hand, non-rising stem gate valves are suitable for locations with limited vertical space. Both gate valve types have unique features and benefits that cater to specific industrial needs. It’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your projects to make an informed decision when choosing between these two gate valve types.