4 Components of Wafer Butterfly Valves: Understanding the Structure

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Parts of Wafer Butterfly Valves
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the inner workings of wafer butterfly valves. In this article, we will delve into the intricate components and functionality of this pivotal valve type. You will gain a deeper understanding of the following key aspects:
- What is a wafer butterfly valve?
- How does it function?
- The fundamental components of a wafer butterfly valve
- Various types of wafer butterfly valves
- The materials used in the construction of these valves
- The advantages and disadvantages of wafer butterfly valves
Understanding the Basics
A wafer butterfly valve serves as a crucial rotational motion device within a piping system, utilizing a rotary disc to control fluid flow. By controlling the orientation of the disc, the valve can either obstruct or permit the flow of fluids. This 90° operation allows for effective flow regulation, making it a versatile solution for a range of applications.
Exploring the Components
Key components of a wafer butterfly valve include the robust valve body, which safeguards the internal mechanisms, and the disc, responsible for regulating fluid flow. The degree of disc opening dictates the flow rate, making it a pivotal element in the valve’s functionality.
What Are Wafer Butterfly Valves?
Wafer butterfly valves are essential components in various industrial applications, providing efficient control over fluid flow. These valves are designed to regulate the flow of liquids in a pipeline and are well-suited for applications that require a tight seal and bi-directional pressure differential protection.
Defining Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer butterfly valves are characterized by their compact size and minimal part count, making them a cost-effective solution for fluid control. Unlike lug-style butterfly valves, wafer valves do not have protruding lugs, allowing them to fit snugly between two pipe flanges. This design prevents the weight of the pipe system from directly impacting the valve body, offering a more economical option for fluid control.
Basic Principles of Operation
The operation of wafer butterfly valves is based on the movement of a disc located within the valve body. This disc, available in concentric or eccentric configurations, regulates the flow of media through the valve. When the valve is in the closed position, the disc forms a tight seal against the valve seat, preventing any backflow and maintaining a secure closure.
These valves are designed to be compatible with electric or pneumatic actuation, offering flexibility in application. Depending on the specific requirements of the fluid being controlled, the materials for the disc and seat are carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
By utilizing precision-machined seals such as gaskets or O-rings, wafer butterfly valves effectively withstand double-directional pressure differentials, making them invaluable components in industrial fluid control systems.
Key Components of Wafer Butterfly Valves
The functionality of wafer butterfly valves relies on several key components that work together to regulate fluid flow effectively. Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending the inner workings of wafer butterfly valves. Let’s delve into the essential elements that constitute these valves.
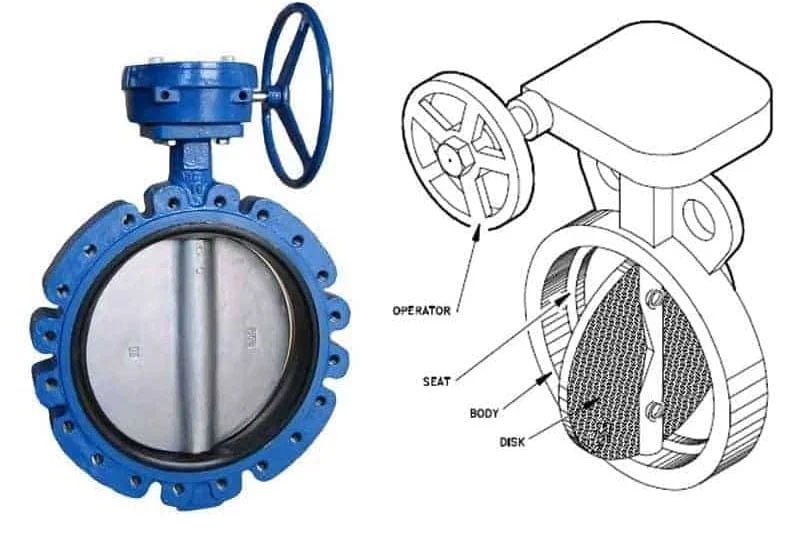
The Valve Body
The valve body of a wafer butterfly valve is designed to fit between two pipe flanges, with the most common body designs being lug and wafer. The compact nature of the wafer body design allows for easy installation and maintenance, making it a popular choice in various industrial applications.
The Disc
In wafer butterfly valves, the disc serves as the primary component responsible for controlling the flow of fluids. Its design and orientation are crucial factors in optimizing flow, enhancing sealing capabilities, and minimizing operating torque. Variations in disc design cater to specific flow requirements, ensuring efficient valve performance.
Stem
The stem of a wafer butterfly valve can manifest as either a one-piece shaft or a two-piece (split-stem) structure. In resilient seated designs, the stem is shielded from the media, enabling the selection of materials based on cost-effectiveness and mechanical properties. This design feature contributes to the valve’s durability and operational reliability.
Seat
The seat of a wafer butterfly valve utilizes an interference fit between the disc edge and the seat to facilitate effective shut-off. Composed of various elastomers or polymers, the seat material is selected to withstand diverse operating conditions. Whether bonded to the body or securely fitted, the seat is integral to ensuring leak-free performance of the valve.
Understanding the intricate interplay of these key components provides a comprehensive grasp of the functionality and reliability of wafer butterfly valves. For businesses seeking reliable valve solutions, these insights can inform the selection of appropriate valves to meet specific operational requirements.
How Wafer Butterfly Valves Function
Wafer butterfly valves function through a quarter-turn mechanism, enabling swift and precise flow control. The efficient design and operation of these valves make them well-suited for numerous industrial applications.
The Quarter-Turn Mechanism
The functionality of wafer butterfly valves is based on a quarter-turn operation, where the disc within the valve turns 90 degrees to regulate the flow of media. This mechanism allows for quick and seamless control, facilitating efficient operation in various flow systems.
From Closed to Open
When the wafer butterfly valve is closed, the disc seals off the flow, preventing the passage of media through the pipeline. Upon opening the valve, the disc rotates a quarter-turn, allowing for unrestricted flow in the system. This swift transition from closed to open positions enables prompt adjustments as per operational requirements.
Adjusting Flow Rates with Precision
Wafer butterfly valves facilitate precise control over flow rates, offering the flexibility to regulate media flow with accuracy. By manipulating the position of the disc, operators can finely adjust flow rates according to specific process demands, ensuring optimal performance and system functionality.
Types and Materials of Wafer Butterfly Valves
When it comes to wafer butterfly valves, the first consideration is understanding the various types available and the materials used in their construction. This knowledge is crucial in choosing the most suitable valve for specific applications.
Common Types of Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer-style butterfly valves are engineered with four holes that align with the connected pipeline and are designed to clamp between two flanges in the pipework. This design feature allows for easy installation and removal, making them a popular choice for many industrial applications. However, it’s essential to note that wafer-style butterfly valves cannot be used as pipe ends or end-of-line service, meaning the entire line must be shut down for maintenance on either side of the valve.
Lug-style butterfly valves, on the other hand, are usually composed of metal such as ductile iron or steel. They feature threaded tapped lugs positioned on the valve flanges for bolt connections. While suitable for end-of-line service, a blind flange is always recommended when using lug-style butterfly valves. These valves are manufactured to be compatible with either pneumatic or electric actuation.
Material Choices for Durability and Performance
The choice of materials for wafer butterfly valves significantly impacts durability and overall performance. Disc and seat materials should be determined based on the specific application and flow media. Common materials used for constructing wafer butterfly valves include rubber or EPDM for creating a strong seal between the valve and flange connection. Additionally, the body of the valve is often constructed from materials such as stainless steel, ductile iron, or cast iron to ensure resilience in various operating conditions and environments.
In industrial applications such as oil and gas, chemical processing, water and wastewater processing, and transportation, food processing, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and HVAC, the choice between lug-style and wafer-style butterfly valves depends on specific project requirements.
Understanding the common types and material choices for wafer butterfly valves is essential in selecting the right valve for a particular application, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and functionality.
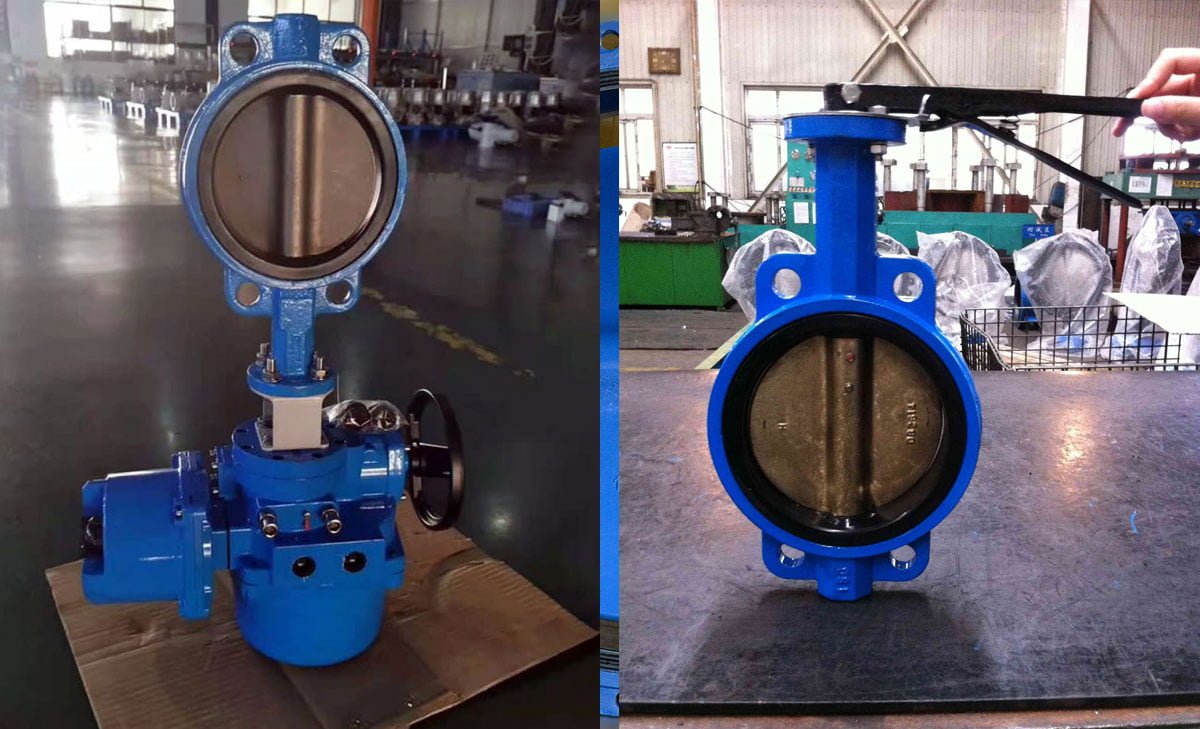

Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation of wafer butterfly valves is crucial to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry best practices for installation to prevent any potential issues.
Proper Installation Practices
When installing wafer butterfly valves, it is important to ensure that the valve is aligned correctly with the pipeline to avoid any operational problems. Additionally, proper gasket installation is critical to prevent leakage. Careful attention should be paid to torque specifications during the installation process to ensure that the valve is securely fastened and aligned.
Routine Maintenance for Longevity
Routine maintenance is essential for prolonging the lifespan of wafer butterfly valves. Regular inspections should be carried out to check for any signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage. Lubrication of the valve components should be conducted as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure smooth operation. Additionally, any accumulation of debris or contaminants should be cleared to prevent potential blockages and operational issues. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule can help in identifying and addressing any potential issues early, thereby extending the lifespan of the wafer butterfly valves.
Advantages of Using Wafer Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves offer a range of advantages, making them a popular choice in industrial applications. Here, we will explore the benefits of using wafer butterfly valves, including their advantages over other valve types.
Benefits in Industrial Applications
Wafer butterfly valves are widely favored in industrial applications for their versatility and performance. They are known for their ability to control flow with precision, making them suitable for a variety of fluid management systems, including those handling corrosive or abrasive substances. Additionally, their streamlined design and efficient operation make them ideal for use in tight spaces where traditional valves may not fit.
These valves are also preferred for their ease of installation, requiring minimal space and providing a cost-effective solution for fluid control. Furthermore, their low maintenance requirements and long service life contribute to their appeal in industrial settings.
Comparing with Other Valve Types
When comparing wafer butterfly valves with other valve types, several distinguishing characteristics come to light. Unlike ball valves, butterfly valves offer a more streamlined flow path, resulting in reduced pressure drop and energy savings. Additionally, their lightweight construction and compact design set them apart from gate valves, which often require more space and maintenance.
In contrast to globe valves, wafer butterfly valves provide quick shutoff and are less prone to leakage, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability. Moreover, their cost-effectiveness and ease of automation make them a favorable choice over traditional gate and globe valves in various industrial applications.
Applications of Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer butterfly valves are widely utilized in various industries for their efficiency and versatility in fluid control. The applications of wafer butterfly valves encompass a broad spectrum of industries and specialized uses, making them integral components in fluid handling systems.
Industries Relying on Wafer Butterfly Valves
- Chemical Industry: Wafer butterfly valves are commonly employed in chemical processing plants for regulating the flow of corrosive fluids such as acids, alkalis, and solvents. Due to their compatibility with a wide range of chemicals, these valves play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of chemical processes.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: In the realm of water and wastewater treatment, wafer butterfly valves are instrumental in controlling the flow of water, sludge, and various treatment chemicals. Their compact design and reliable performance make them ideal for use in water distribution systems, sewage treatment plants, and desalination facilities.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on wafer butterfly valves to modulate the flow of air, water, and other fluids within ducts and pipes. These valves contribute to the precise regulation of temperature, humidity, and air quality in residential, commercial, and industrial environments.
Specialized Uses in Fluid Control
- Fire Protection Systems: Wafer butterfly valves are integral components of fire protection systems, where they serve to isolate or regulate the flow of water in sprinkler and deluge systems. Their quick-acting and reliable nature makes them essential for safeguarding properties and ensuring swift response to fire emergencies.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Within the food and beverage industry, wafer butterfly valves are utilized for handling various liquids and gases during production and packaging processes. These valves adhere to stringent hygienic standards and facilitate the seamless control of ingredients and by-products in food manufacturing facilities.
- Oil and Gas Operations: In the oil and gas sector, wafer butterfly valves are employed in refining, distribution, and storage facilities to manage the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products. Their ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures makes them indispensable for ensuring the safety and efficiency of hydrocarbon processing operations.
The unique capabilities of wafer butterfly valves make them indispensable across diverse industrial sectors, and their specialized uses underscore their significance in fluid control applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the inner workings of wafer butterfly valves provides valuable insight into the components and functionality of these essential pipeline control devices. From the rotational motion mechanism to the key components such as the valve body and disc, the intricate design of butterfly valves enables precise fluid regulation in various pipeline systems. As industries continue to rely on efficient flow control, grasping the fundamentals of butterfly valves is indispensable for engineers, maintenance professionals, and decision-makers seeking optimal fluid management solutions.