Gate Valve vs. Globe Valve: A Comparison of Functionality

Table of Contents
ToggleGate Valve vs. Globe Valve: An In-Depth Comparison of Functionality
When it comes to industrial applications, gate valves and globe valves play significant roles in controlling the flow of media. While they may appear similar, these valves function differently, each with unique characteristics and purposes. In this article, we will explore the distinct functionalities of gate valves and globe valves, and analyze the major differences between the two, shedding light on their individual applications and advantages.
Design and Functionality
- Gate valve: Linear motion valve that uses a wedge-shaped gate to control flow.
- Globe valve: Linear motion valve with a plug or disc that moves perpendicular to the flow to regulate fluid.
Flow Characteristics
- Gate valve: Suitable for on/off service, provides minimal pressure drop when fully open.
- Globe valve: Ideal for regulating flow, offers better throttling ability and precise control.
Applications
- Gate valve: Commonly used in applications where a tight shutoff is required, such as in the oil and gas industry.
- Globe valve: Widely used in systems that require frequent adjustments and accurate flow control, such as in HVAC systems.
Pressure and Temperature Limitations
- Gate valve: Can handle high pressure and temperature, but may experience leakage if used for throttling.
- Globe valve: Suitable for moderate pressure and temperature, effective in handling corrosive and erosive fluids.
Maintenance and Repair
- Gate valve: Relatively easier to maintain and repair due to simpler design and fewer moving parts.
- Globe valve: More complex internal structure may require more frequent maintenance and inspection.
Cost and Size
- Gate valve: Typically larger and heavier, may be more cost-effective for high-pressure applications.
- Globe valve: Smaller and lighter, suitable for space-constrained installations and systems with lower pressure requirements.
Sealing Mechanism
- Gate valve: Relies on metal-to-metal contact for sealing, which can be susceptible to wear and corrosion.
- Globe valve: Uses a soft or metal seating for sealing, providing better resistance to wear and corrosion.
Flow Direction
- Gate valve: Unidirectional flow, suitable for applications with strictly defined flow direction.
- Globe valve: Bi-directional flow capability, allowing flexibility in installation and operation.
Noise and Vibration
- Gate valve: Tends to generate less noise and vibration when fully open, but may experience water hammer during rapid operation.
- Globe valve: Offers better dampening of flow-induced noise and vibration, especially in partially open positions.
Accessibility and Visibility
- Gate valve: Provides clear visual indication of the valve’s position, facilitating quick identification and operation.
- Globe valve: Internal components may obstruct visibility, requiring additional measures for position monitoring and maintenance.
Understanding Valve Basics
Valves serve as crucial components in controlling, regulating, and directing flow within various systems and processes. They play a significant role in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of liquids, gases, and solids through piping systems. This section will delve into the fundamental concepts of gate valves and globe valves, shedding light on their distinctive functionalities and applications.
Defining Gate Valves
Gate valves, characterized by a linear motion of the gate to start or stop flow, are widely acclaimed for their ability to provide unrestricted flow when fully open. These valves are designed to minimize pressure drop and ensure a tight seal, making them ideal for applications requiring a straight-line flow of fluid with minimal restriction. The distinct advantage of gate valves lies in their ability to offer a tight shutoff, making them well-suited for applications where leakage prevention is paramount.
Defining Globe Valves
Globe valves, on the other hand, operate using a linear motion to regulate and control the flow of fluid within a pipeline. Their distinct design features a globe-shaped body, providing an efficient means of throttling flow and regulating pressure. Globe valves are revered for their capability to finely tune the flow of media, making them well-suited for applications that demand precise control and adjustment of fluid flow. Moreover, their composition allows for simple bonnet assembly and disassembly, facilitating streamlined maintenance and repair operations.

This foundational understanding of gate valves and globe valves sets the stage for a comprehensive comparison, unraveling the unique features and operational variances that distinguish these two critical components in fluid control systems.
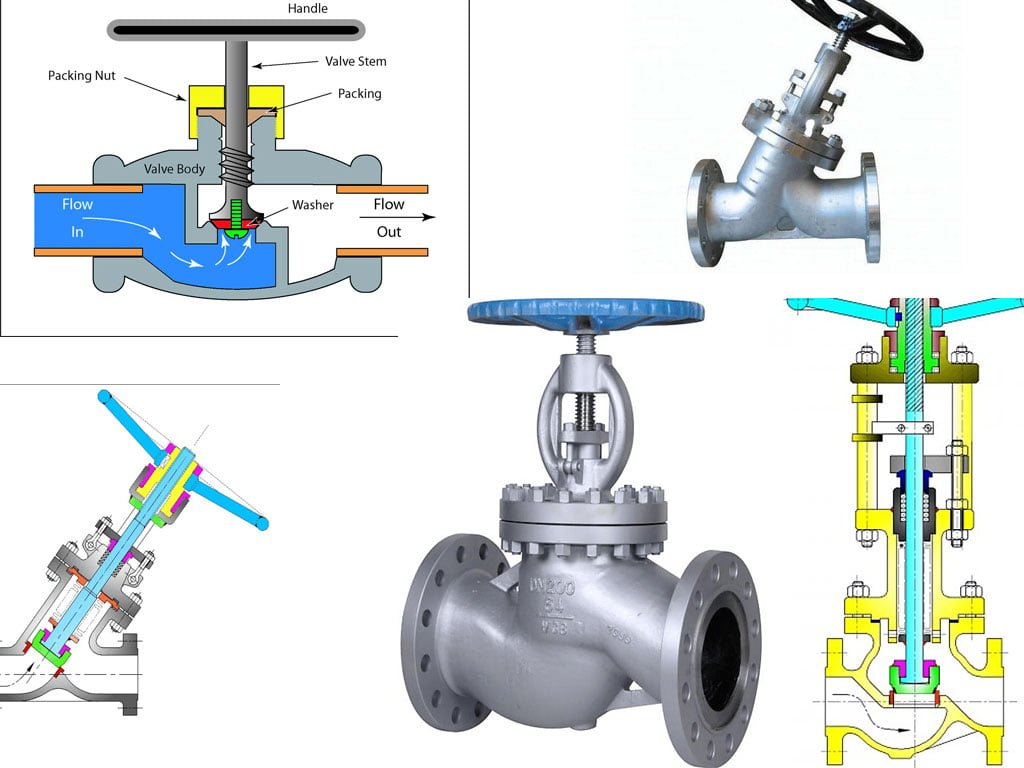
The Design of Gate Valves
A gate valve is a type of control valve that regulates the flow of a fluid by the raising and lowering of a gate within the valve. Gate valves generally consist of several key parts, including the handwheel for manual operation, stem for gate movement, gasket for sealing, bonnet for covering the valve internals, valve body for housing the gate and other parts, flange for connection, and the gate itself. The gate valve’s design allows for a straight-through unobstructed passageway, resulting in minimal pressure loss, and also enables the passage of tools like pigs during cleaning procedures.
Operation and Use Cases for Gate Valves
To operate a gate valve, the handwheel is turned to raise or lower the gate along the stem using threads. This action either opens or closes the valve fully, allowing for an unobstructed flow or complete blockage of the fluid. Gate valves are best suited for applications where the flow needs to be fully on or off without the need for flow regulation. Common use cases for gate valves include high-pressure systems, steam lines, and in situations where minimal pressure drop is a priority.
Advantages of Using Gate Valves
The design of gate valves offers several advantages, including low pressure loss due to the unobstructed flow path, efficient sealing, and the ability to function in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. Additionally, gate valves can accommodate a wide range of fluids, making them versatile for various industrial applications.
Limitations of Gate Valves
While gate valves have numerous advantages, they also have limitations. Gate valves are not suitable for throttling or regulating flow due to their on/off nature. Additionally, they are slower to operate compared to quarter-turn valves and may require multiple rotations to fully open or close, making them less suitable for applications where quick adjustments are necessary.
Globe Valves Explored
The Design of Globe Valves
Globe valves are designed with a movable disk or plug that regulates the flow of fluid through the valve. The body of the globe valve is typically spherical, resembling a globe, hence the name. The interior of the globe valve contains a horizontal or angled seat, which the movable disk or plug presses against to control the flow.
How Globe Valves Function
Globe valves function by raising or lowering the movable disk or plug to increase or decrease the flow of fluid. This upward and downward motion allows for more precise regulation of the flow compared to other types of valves. When the valve is fully open, the flow of fluid is straight with minimal restrictions.
Benefits of Globe Valves in Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, globe valves are favored for their ability to provide accurate flow control and to shut off the flow completely when needed. They are also suitable for regulating the flow of high-pressure and high-temperature fluids, making them versatile for various industrial applications. Additionally, globe valves are less prone to erosion compared to other types of valves, enhancing their longevity and reliability.
Drawbacks of Globe Valves
One drawback of globe valves is their comparatively slower operation due to the multiple turns required to open or close the valve fully. This can result in increased pressure drop and turbulence in the system. Additionally, globe valves may be more susceptible to damage in systems with high flow rates and frequent operation due to the nature of their design.

Key Differences Between Gate and Globe Valves
Gate and globe valves are both essential components in fluid control systems, each serving distinct purposes based on their design and functionality. Understanding the key differences between these valves is crucial for making informed decisions in various industrial and commercial applications.
Flow Direction and Fluid Dynamics
Gate valves are designed for on/off service and offer minimal obstruction to the flow of fluids, providing a straight-through unobstructed path. In contrast, globe valves are designed to regulate flow, with a more intricate internal structure that facilitates a change in the direction of flow. The distinct flow patterns of gate and globe valves make them suitable for different operational requirements, depending on the fluid dynamics and flow direction within the system.
Pressure Drop Considerations
When it comes to pressure drop, gate valves typically have minimal interference with the fluid flow, resulting in low pressure drop across the valve. On the other hand, globe valves are equipped with a more complex internal structure, causing a higher pressure drop compared to gate valves. Understanding the pressure drop considerations associated with each valve type is crucial for optimizing system performance and efficiency.
Throttling Capabilities and Applications
Gate valves are not suitable for precise flow regulation or throttling due to their binary on/off operation. In contrast, globe valves offer superior throttling capabilities, allowing for precise control of the flow rate. The distinct throttling capabilities of these valves determine their applications, with gate valves being ideal for applications requiring full flow or complete shut-off, while globe valves are better suited for applications that demand precise flow control and throttling.
Sealing and Leakage Prevention
Gate valves utilize parallel and wedge-shaped gates to establish a seal against the valve seats, providing effective shut-off capabilities with minimal leakage. In contrast, globe valves employ a plug and seat arrangement, enabling a more reliable sealing mechanism to prevent leakage during operation. Understanding the sealing mechanisms of gate and globe valves is critical for ensuring optimal performance and minimizing the risk of fluid leakage within the system.
By recognizing the differences in flow direction, pressure drop considerations, throttling capabilities, and sealing mechanisms between gate and globe valves, professionals can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable valve for specific applications. These distinctions play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of fluid control systems across various industries and sectors.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Gate and Globe Valves
Valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of fluids and gases in various industries. When it comes to selecting the right valve for specific applications, there are several important factors to take into account.
Industry-Specific Valve Requirements
Different industries have specific valve requirements based on the nature of the materials being handled and the operational conditions. For instance, in industries dealing with corrosive or abrasive fluids, such as chemical processing or mining, the choice of valve material is critical to ensure compatibility and longevity. Additionally, industries with high-pressure or high-temperature environments, such as oil and gas or power generation, need valves that can withstand these extreme conditions without compromising performance.
Maintenance and Durability Concerns
The maintenance and durability of valves are crucial considerations for long-term cost-effectiveness. Some valves may require frequent maintenance due to their design complexity or susceptibility to wear and tear, while others are designed for minimal maintenance and extended service life. Understanding the maintenance requirements and durability of gate and globe valves is essential for making an informed decision based on the specific needs of the application.
By carefully evaluating the factors mentioned above, businesses can make well-informed decisions when choosing between gate and globe valves for their unique operational requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gate valves and globe valves each offer unique functionalities and benefits in industrial applications. Gate valves are ideal for isolating media with tight sealing requirements, providing minimal pressure drops, and offering limited throttling capacity. On the other hand, globe valves excel at regulating media flow, maintaining a tight seal with minimal leakage, and are suitable for applications prioritizing safety and leak prevention. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these valves is crucial in selecting the most appropriate option for specific industrial needs.