Understanding Needle Valves: A Comprehensive Guide

Needle valves play a crucial role in controlling flow within various industrial applications. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a detailed understanding of needle valves, their historical development, and their importance in industrial settings.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Needle Valves?
Needle valves are precision valves used to regulate the flow of gas or liquid in a system. They are named for their long, needle-like stems that provide precise control over the rate of flow. These valves are designed to provide fine adjustments, making them ideal for applications where a small flow rate is required.
Importance in Industrial Applications
Needle valves are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and manufacturing. Their ability to finely control flow makes them essential in processes where precision is paramount, such as in metering, calibration, and pressure instrument isolation.
Brief History and Development
The concept of needle valves dates back to the early 20th century, with initial designs focusing on creating a valve that could offer precise control over flow rates. Over time, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of needle valves that can withstand high pressures and corrosive environments. The evolution of needle valves has been driven by the increasing demand for accuracy and reliability in industrial processes.
Needle valves are integral components in industrial systems, providing the precise flow control necessary for various applications. Understanding the history and development of needle valves helps to appreciate their significance in modern industrial processes. With their ability to regulate flow with exceptional precision, needle valves continue to be indispensable in ensuring the efficiency and safety of industrial operations.
Different Types of Needle Valves
Needle valves are essential components in many industries, offering precise control over flow rates. Understanding the various types of needle valves can help in selecting the most suitable option for specific applications. Here are the different classifications and design variations of needle valves:
General Classification
Needle valves are generally classified based on their structure and application. The most common types include integral bonnet, screwed bonnet, and union bonnet needle valves. Each type has unique features that make them suitable for different working conditions and environments.

Different Design Variations of Needle Valves
Soft Seat
Soft seat needle valves are designed with a soft elastomeric material, such as Teflon or Viton, to create a tight seal. These valves are ideal for applications that require bubble-tight shut-off and are commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical processing.
Regulating
Regulating needle valves are specifically designed for precise flow control. They are often used in instrumentation and control systems where accurate regulation of fluid flow is crucial. These valves feature a fine-threaded stem that allows for minute adjustments, making them suitable for applications where precision is paramount.
Plunger Valves
Plunger needle valves, also known as packless valves, use a unique plunger design to control flow. Plunger valves are commonly used in high-pressure applications where conventional needle valves may not withstand the extreme operating conditions. Plunger valves offer reliable sealing and are widely utilized in hydraulic systems and industrial equipment.
Understanding the different types of needle valves can help in making informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate valve for specific applications. Whether it’s for controlling flow rates, regulating pressure, or ensuring tight shut-off, having a clear understanding of the various needle valve types is crucial in optimizing operational efficiency and safety.
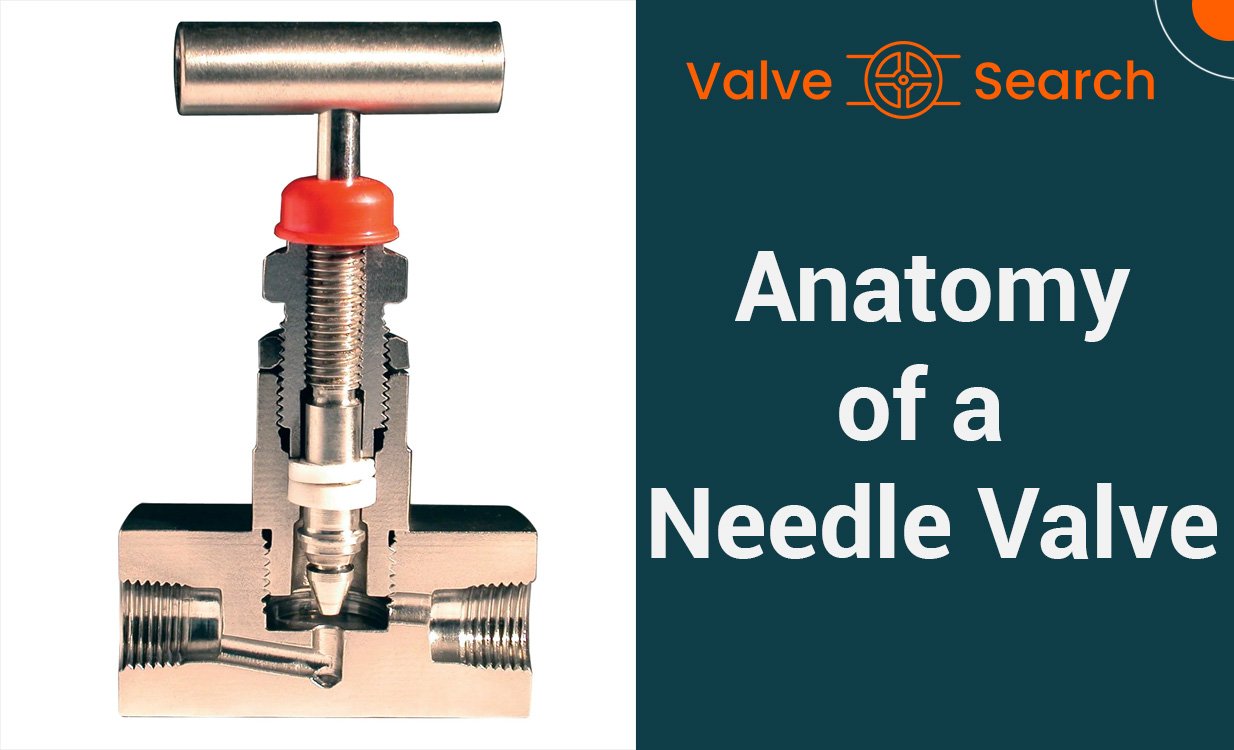
Components of Needle Valves
Needle valves are precision instruments used to regulate the flow of gases and liquids in various industries. Understanding the components of these valves is crucial for maintaining and repairing these important pieces of equipment. Here is a detailed breakdown of the parts and material considerations for needle valves:
Detailed Breakdown of Parts
1. Body
The body of a needle valve is the main housing that holds all the internal components together. It is typically made of durable materials such as stainless steel or brass to withstand high pressure and corrosive environments.
2. Bonnet
The bonnet of the valve is the top part that encloses the valve stem and provides a seal to prevent leaks. It is usually threaded or bolted to the body and is designed to withstand the pressure exerted by the fluid or gas passing through the valve.
3. Stem
The stem is the part of the needle valve that connects the handwheel or actuator to the internal components, allowing the user to control the flow of the fluid or gas. It is crucial for the smooth operation of the valve and is often made of stainless steel for strength and corrosion resistance.
4. Seat
The seat of a needle valve is the sealing surface that the needle or plunger comes into contact with to shut off the flow. It is typically made of hard materials such as ceramic or Stellite to withstand wear and ensure a tight seal.
5. Packing
The packing of a needle valve provides a seal around the stem to prevent leaks. It is usually made of materials like PTFE (Teflon) or graphite to provide a reliable seal while allowing the stem to move smoothly.
Material Considerations
When considering the materials for needle valve components, factors such as the type of fluid or gas being controlled, pressure and temperature requirements, and environmental conditions must be taken into account. Stainless steel, brass, and alloys are commonly used for the body and bonnet, while the seat and packing materials are carefully selected based on compatibility with the fluid or gas and the operating conditions.
Components and material considerations of these valves is essential for selecting the right valve for specific applications and ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Parts of needle valves, including the body, bonnet, stem, seat, and packing, play crucial roles in the functionality and reliability of these precision instruments. Material considerations are equally important to ensure that the valve can withstand the specific operating conditions and fluid or gas properties. By understanding these components and considerations, industries can make informed decisions when choosing, maintaining, and repairing needle valves.
Working Principles
Flow Control Mechanism
Needle valves use a tapered pin to gradually open and close the orifice, allowing precise control of flow rates.
The fine threading of the stem and the small orifice diameter enable accurate adjustments, making these valves ideal for applications requiring precise flow control.
Operating Pressures and Temperatures
- Needle valves are designed to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions, making them suitable for applications where other valve types may not be able to perform effectively.
- The ability to handle extreme operating conditions makes these valves a critical component in demanding industrial processes.
Comparison with Other Valve Types
- Compared to ball valves and gate valves, needle valves provide finer control over flow rates, especially at low flow levels.
- They offer superior throttling capabilities, making them the preferred choice for applications that demand precise regulation of fluid flow.
Applications
Industry-Specific Uses
- Oil & Gas: Needle valves are widely used in the oil and gas industry for controlling flow in pipelines, wellheads, and pressure monitoring systems.
- Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, needle valves are essential for regulating flow in corrosive and abrasive fluid handling systems.
- Aerospace: Needle valves play a crucial role in aerospace applications, where precise control of fuel and hydraulic fluids is necessary for safe and efficient operation.
Considerations for Each Application
- Oil & Gas: When selecting needle valves for oil and gas applications, factors such as material compatibility, pressure ratings, and resistance to sour gas environments must be carefully considered.
- Chemical Processing: In chemical processing facilities, resistance to chemical corrosion, material compatibility, and compliance with industry standards are key considerations when choosing needle valves.
- Aerospace: Needle valves used in aerospace applications must meet stringent quality and safety standards, including reliability under extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
Needle valves are versatile components that offer precise flow control in various industrial settings. Understanding their working principles, applications, and industry-specific considerations is crucial for selecting the right valve for specific operational requirements.
Needle Valves: Advantages, Selection, Installation, and Maintenance
Needle valves are essential components in various industrial applications, offering precise flow control and reliable performance. Understanding the benefits, limitations, selection criteria, and maintenance requirements of them is crucial for optimizing their functionality and ensuring efficient operations.
Benefits of using needle valves
- Precise Flow Control: Needle valves provide exceptional control over flow rates, making them ideal for applications requiring fine adjustments in fluid or gas flow.
- Leak Tightness: Their design allows for tight shut-off, minimizing the risk of leakage and ensuring system integrity.
- High Pressure and Temperature Capability: Needle valves are capable of withstanding high pressure and temperature conditions, making them suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Potential drawbacks in certain scenarios
- Flow Restriction: While needle valves offer precise control, they can also cause significant pressure drops, impacting overall system efficiency.
- Susceptibility to Contamination: The narrow flow path of needle valves can make them susceptible to clogging and damage from particulate matter in the fluid.
- Limited Flow Capacity: In applications requiring high flow rates, they may not be the most efficient choice due to their inherent flow restrictions.
Maintenance requirements
- Regular Inspections: Periodic visual inspections and functional checks are essential to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage.
- Proper Lubrication: Applying the appropriate lubricant to the valve stem and threads is critical to ensure smooth operation and prevent seizing.
- Seal Replacement: Over time, the valve seals may degrade, necessitating timely replacement to maintain leak-tight performance.
Selecting the Right Needle Valve
- Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the valve materials with the fluid or gas being handled to prevent corrosion or chemical reactions.
- Operating Conditions: Evaluate the temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions to ensure the selected valve can withstand the specific application requirements.
- Flow Requirements: Determine the precise flow control needs to select a needle valve with the appropriate Cv (flow coefficient) and pressure ratings.
Sizing guidelines
Cv Calculation: Calculate the required Cv value based on the desired flow rate and pressure drop to size the needle valve correctly for the application.
Installation and Maintenance
- Proper Installation Procedures: Follow manufacturer guidelines for correct installation, including proper alignment, tightening torque, and leak testing.
- Routine Maintenance Practices: Develop a maintenance schedule for regular cleaning, lubrication, and seal inspections to prolong the valve’s service life.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Be familiar with identifying and addressing common issues such as leaks, sticking, or excessive friction in valve operation.
Needle Valves FAQ
What is a needle valve?
A needle valve is a type of valve used to accurately control the flow of a liquid or gas in a system. It consists of a slender, tapered needle-like plunger that fits into a matching seat.
How does a needle valve work?
A needle valve works by using the threaded stem to finely adjust the space between the plunger and the seat, thus controlling the flow of fluid or gas through the valve. This precise control allows for accurate regulation of flow rates.
What does a needle valve do?
A needle valve is designed to provide precise flow control in applications where accuracy is critical. It is commonly used in situations where the flow needs to be finely adjusted or shut off completely.
Can a needle valve regulate pressure?
While a needle valve is primarily used for flow control, it can also be used to regulate pressure to some extent. By controlling the flow, a needle valve indirectly affects the pressure in the system, making it useful for pressure regulation in certain applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, needle valves play a crucial role in achieving precise flow control and system integrity in various industrial processes. Understanding their benefits, limitations, proper selection criteria, and maintenance practices is essential for maximizing their performance. As industries continue to evolve, ongoing developments in needle valve technology are anticipated to further enhance their capabilities and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth understanding of needle valves, shedding light on their critical role in fluid control applications. By grasping the nuances of needle and plunger valves, you are better prepared to navigate the complexities of fluid regulation and enhance the reliability of your systems.