Pinch Valves: Mega Guide – Working, Parts, Types, Applications
Table of Contents
ToggleComprehensive Guide to Pinch Valves
Pinch valves are essential components in various industries, providing reliable control of flow in pipelines. Understanding how pinch valves work, their technical aspects, parts, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, selection criteria, and operating parameters is crucial for their effective implementation. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate details of pinch valves to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance in your industrial processes.
Importance of Pinch Valves in Flow Systems
Pinch valves are simple and reliable flow control devices that are particularly well-suited for handling abrasive or corrosive fluids. The basic working principle of a pinch valve involves the use of a flexible rubber sleeve that is pinched to shut off the flow and released to allow the flow of the media.
Basic Working Principle of Pinch Valves
The pinch valve operates by applying pressure to the flexible rubber sleeve, which effectively constricts the flow of the media passing through the valve. When the pressure is released, the sleeve returns to its original position, thereby allowing the media to flow freely. This straightforward mechanism makes these valves ideal for applications involving thick fluids, slurries, and other challenging media.
The Core Components of a Pinch Valve
The core components of a pinch valve include the housing, the rubber sleeve, and the end connections. The sleeve, made of durable and flexible material, serves as the primary component that comes into contact with the flowing media, effectively isolating it from the rest of the valve. The end connections provide structural support and facilitate the attachment of the valve within a system.
Housing: The outer structure of the pinch valve, the housing, serves as the foundation that holds and encases the other vital components of the valve. It provides protection and support for the internal mechanisms, ensuring the proper operation of the valve.
Elastomeric Rubber Sleeve: This component is the point of contact with the media flowing through the valve. Inserted into the housing from the inlet to the outlet, the elastomeric rubber sleeve is designed to be pinched or “squeezed” to effectively regulate the flow of the media. Its unique properties allow for flexibility and resilience, enabling it to withstand varying pressures and conditions.
End Connections: Attached at each end of the valve, the end connections play a crucial role in providing support and facilitating the connection of the valve within the system. These connections can take the form of screws, bolts, or threads, depending on the specific requirements and applications of the pinch valve.
The valve operates by applying air or hydraulic pressure to push down the elastomeric rubber sleeve, causing it to pinch and restrict the flow, closing the valve. Releasing the external pressure allows the flowing media and the rubber’s rebounding property to fully open the valve.
Understanding the housing, elastomeric rubber sleeve, and end connections of a pinch valve is crucial for comprehending its function and ensuring optimal performance in industrial settings. Proper maintenance and care of these components are essential for the long-term efficiency of the valves in various applications.
Pinch (squeeze) valves come in various configurations, such as mechanical or automatic, each tailored to specific operational requirements. Mechanical pinch valves are actuated manually through the rotation of a handwheel, while automatic pinch valves utilize compressed air, hydraulic fluid, or solenoid for operation. These versatile valves find use across a spectrum of industries, from mining and chemical processing to wastewater treatment and pharmaceutical production.

Major Functions of Pinch Valves
Manual Pinch Valve
- Simple Design: Manual pinch valves have a straightforward design, consisting of a rubber sleeve that can be pinched to control the flow of fluid.
- Cost-Effective: These valves are cost-effective due to their simple design, which reduces manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Flow Control: Manual valves offer precise control over the flow of various types of fluids, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Minimal Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, manual pinch valves require minimal maintenance, leading to reduced downtime and overall lower maintenance costs.
Pneumatic Pinch Valve
- Pneumatic Operation: Utilizes compressed air or gas to open and close the valve, providing quick and reliable actuation.
- Easy Installation and Integration: Pneumatic pinch valves are relatively easy to install and integrate into existing systems, offering a practical solution.
- Corrosion Resistance: Constructed with materials such as rubber and corrosion-resistant metals, ensuring durability and longevity in aggressive environments.
- Solenoid Control: Integrates with solenoid valves for remote and automated operation, enhancing precision and efficiency in industrial processes.
Hydraulic Pinch Valve
- High Pressure Rating: This valve is designed to withstand high pressure, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications.
- Bubble-Tight Seal: It provides a reliable bubble-tight seal, ensuring leak-free performance and enhancing operational safety.
- Corrosion Resistance: With materials designed to resist corrosion, the hydraulic pinch valve offers long-term durability in harsh operating environments.
- Quick Response Time: Pinch (squeeze) valve features a quick response time, enabling rapid opening and closing for improved process control.
Electric Pinch Valve
- Fast Response Time: Electric pinch valves offer rapid response times, allowing for quick opening and closing to control the flow of materials.
- Excellent Control Accuracy: These valves provide precise regulation of flow, making them suitable for applications requiring accurate fluid control.
- Bi-Directional Flow Capability: Electric pinch (squeeze) valves can effectively control the flow of fluids in both directions, offering versatility in various industrial settings.
- Corrosion-Resistant Construction: Electric squeeze valves are constructed from durable and corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring longevity and reliability in corrosive environments.
Technical Specifications of Pinch Valves
Valve Size
Pinch valves are available in a range of sizes, typically from ¼ inch to 12 inches, to accommodate different flow requirements.
Valve Body Material
The material of the valve body is a critical specification, with options including aluminum, stainless steel, and various types of rubber, each offering different chemical resistance and durability.
Sleeve Material
The material of the valve sleeve determines its compatibility with different fluids. Options include natural rubber, EPDM, neoprene, and others to ensure compatibility with specific applications.
Operating Pressure
Pinch valves are designed to operate within specific pressure ranges, typically from 0 to 100 PSI, although higher pressure variants are available for specialized applications.
Operating Temperature
Understanding the temperature range within which the pinch valve will operate is essential for ensuring its longevity and preventing any material degradation or failure.
Valve Actuation
They can be actuated manually, pneumatically, or electronically, with each method offering different levels of control and automation.
Flow Rate
The maximum flow rate of this valve is a crucial specification to consider when selecting a valve for a specific application, ensuring it can handle the required volume of fluid.
Connection Type
They are available with different connection types, including threaded, flanged, and tri-clamp, allowing for easy integration into existing piping systems.
Certifications and Standards
Consideration of industry-specific certifications and standards, such as FDA compliance for food and beverage applications or ATEX certification for hazardous environments, is essential for regulatory compliance.
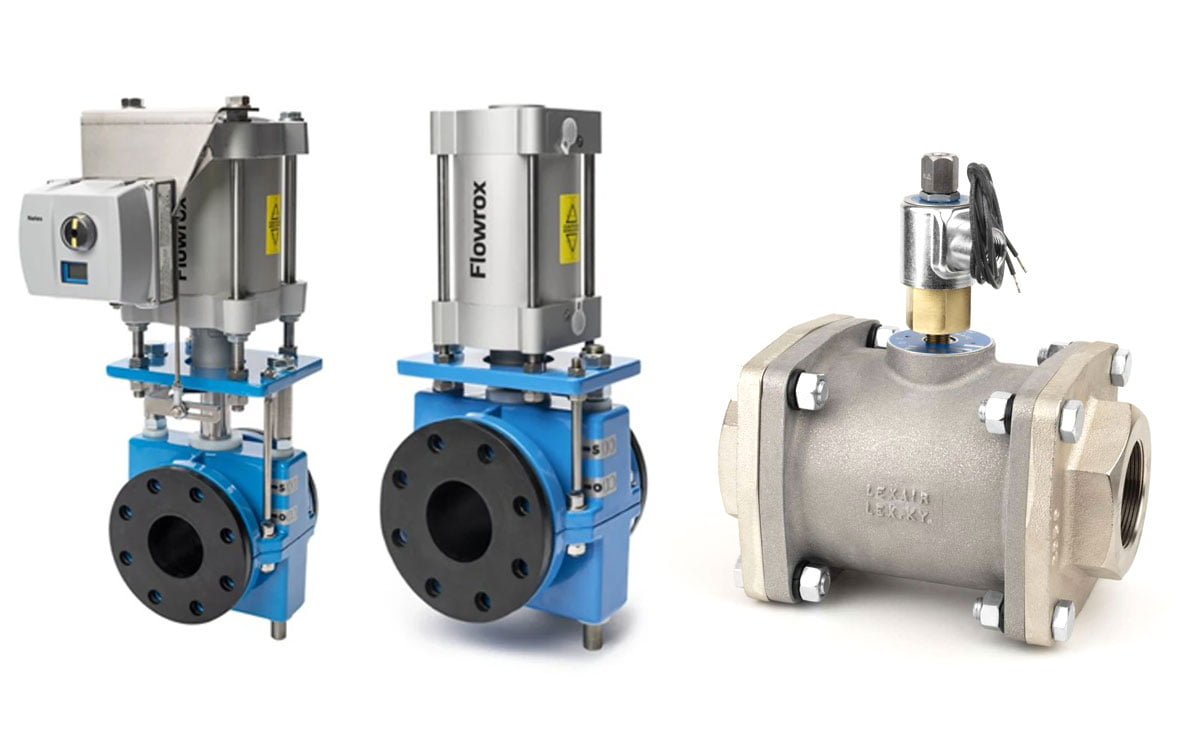

Image Credits: Valmet Forward | Flowrox | Lexair Inc.
4 Types of Pinch Valves
Pinch (squeeze) valves are versatile and can be classified into different types based on their actuation mechanisms. Each type is designed to suit specific application requirements.
Manual Pinch Valve
Manual pinch valves are operated by a manual wheel or lever. This valve is simple in design and cost-effective, making it suitable for applications where the automation of valve operation is not necessary. Manual pinch/squeeze valves are commonly used in small-scale or intermittent flow control applications.
Air-Operated / Pneumatic Pinch Valve
Air-operated pinch valves, also known as pneumatic pinch valves, are actuated by compressed air. When the air pressure is applied or released, it causes the valve to open or close, regulating the flow of the media. These valves are widely used in industries where remote or automated control of the flow is essential, offering quick and reliable operation.
Hydraulic Pinch Valve
Hydraulic pinch valves are actuated by hydraulic pressure, making them suitable for applications where a high level of force is required to control the flow. These valves are known for their robustness and ability to handle demanding operating conditions, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as mining, slurry transportation, and abrasive material handling.
Electric Pinch Valve
Electric pinch valves utilize an electric motor to actuate the pinching mechanism. These valves offer precise control over the flow and can be integrated into automated control systems. Electric pinch valves are used in applications where accurate flow modulation and remote operation are critical, such as in water treatment plants, pharmaceutical processing, and food and beverage production.
Each type of pinch valve offers unique advantages and is selected based on the specific requirements of the application, including the nature of the media, operating conditions, and the level of automation needed. Understanding the differences between these types of these valves is crucial for selecting the most suitable valve for a particular process.
Materials suitable for pinch valves
Pinch valves are highly efficient in handling a wide range of materials such as cement, fly ash, mining minerals, calcium carbonate, PVC, plastic pellets, plastic powders, polyethylene, ceramic powders, alumina, bentonite, bauxite, coal, cement clinker, gypsum, perlite, kaolin, limestone, marble powder, soda ash, quartz, urea, sodium sulfate, wheat, flour, animal feed, seed, corn, rice, sugar, and salt in powder, pellet, granular, and aggregate forms.
Pinch (squeeze) valves are specifically designed to provide precise control and isolation of the flow, making them ideal for various industrial applications where reliable material handling is crucial. The pinch valve’s ability to handle such a diverse range of materials makes it a versatile and essential component in industrial processes.
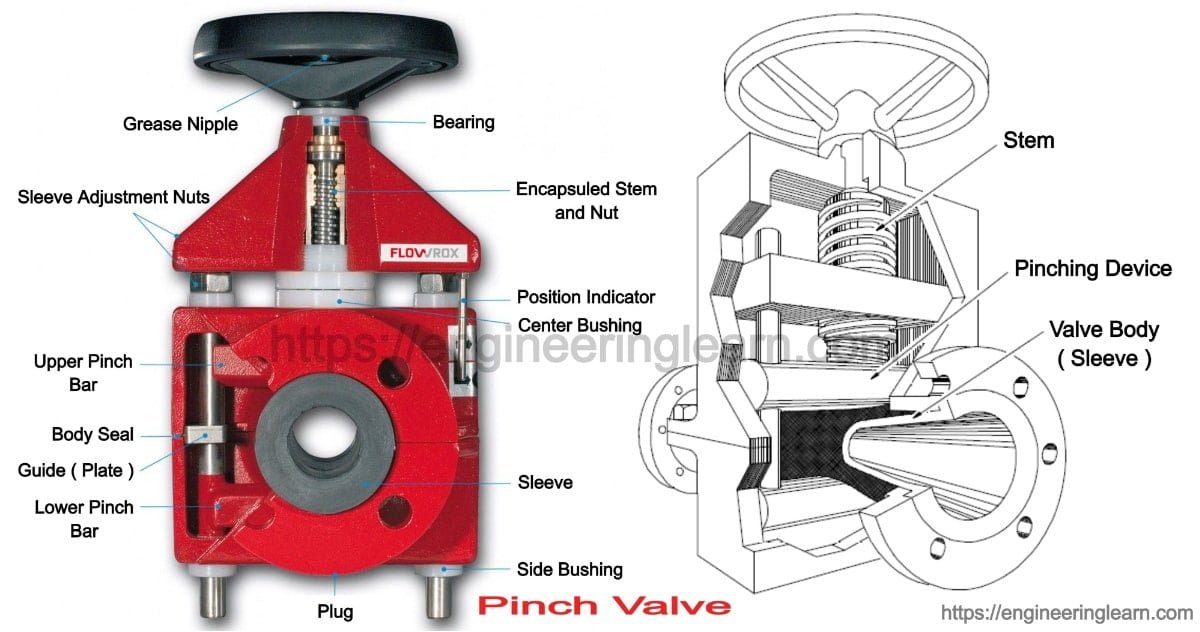
Image Credit: engineeringlearner.com
8 Pinch Valve Applications Across Industries
These valves are crucial components in fluid control systems across a wide range of industries. Their unique design and functionality make them suitable for various applications.
Here are eight key industries where pinch valves are extensively used:
1. Water and Wastewater Treatment
Pinch valves play a vital role in water and wastewater treatment processes, where they are used for regulating the flow of liquids, sludge, and slurries. Their ability to handle abrasive and corrosive materials makes them ideal for this demanding application.
2. Mining and Mineral Processing
In the mining and mineral processing industry, pinch valves are utilized for controlling the flow of abrasive materials such as slurries, tailings, and mine dewatering processes. Their robust construction enables them to withstand the harsh conditions prevalent in these operations.
3. Chemical and Petrochemical
Pinch valves are widely employed in chemical and petrochemical plants for managing the flow of corrosive and aggressive chemicals. Their versatility and resistance to chemical corrosion make them indispensable in ensuring the safe and efficient handling of various substances.
4. Food and Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, these valves find applications in handling food products, beverages, and sanitary fluids. Their hygienic design and ease of maintenance make them suitable for use in compliance with stringent hygiene standards.
5. Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
Pinch valves play a critical role in pharmaceutical and biotechnology processes, where they are used to control the flow of sensitive liquids and fluids. Their ability to provide a contamination-free environment aligns with the strict regulatory requirements of these industries.
6. Power Generation
In power plants, pinch (squeeze) valves are utilized for controlling the flow of abrasive slurries, fly ash, and other challenging media. Their reliability and low maintenance requirements make them well-suited for critical applications in power generation facilities.
7. Pulp and Paper
Pinch (squeeze) valves are integral to the pulp and paper industry, where they are used for regulating the flow of pulp, paper stock, and various chemicals involved in the production process. Their resilience to abrasive substances contributes to improved operational efficiency in this sector.
8. Automotive and Transportation
In the automotive and transportation sector, squeeze valves are employed in applications such as vehicle wash systems, fuel handling, and air brake systems. Their ability to handle diverse fluids and adapt to varying operating conditions makes them essential components in these applications.
The versatility and reliability of these valves make them indispensable across diverse industries, where they contribute to efficient fluid control and processing. Understanding the wide-ranging applications of these valves underscores their significance in ensuring the seamless operation of fluid handling systems in various industrial settings.
FAQ: Pinch Valves – All The Questions
A pinch valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of a fluid by pinching a flexible, elastomeric tube or sleeve to stop or regulate the flow.
The primary purpose of a pinch valve is to provide a reliable and cost-effective method for controlling the flow of abrasive, corrosive, and viscous fluids. It is designed to minimize maintenance requirements and ensure efficient operation in challenging industrial environments.
A pinch valve works by using a mechanism to pinch a flexible tube or rubber sleeve, thereby obstructing the flow of the fluid passing through it. When the valve is open, the tube or sleeve is in its relaxed state, allowing for unrestricted flow. When the valve is closed, the tube or sleeve is compressed to cut off the flow.
A pinch valve is commonly used in applications involving abrasive, corrosive, or viscous fluids. It is also effective for handling slurries, liquids with large solids, and applications where the prevention of cross-contamination is crucial.
A pneumatic pinch valve operates using air pressure to control the opening and closing of the valve. When air pressure is applied, the valve mechanism pinches the sleeve, effectively closing the valve. Releasing the air pressure allows the valve to open again.
They are highly effective in handling abrasive and corrosive materials due to the simplicity of their design and the ability to isolate the flowing media from the valve components. They are also known for their quick and easy maintenance, making them a popular choice in various industries.
The sleeve on a pinch valve is the flexible, elastomeric tube that is pinched to control the flow of the fluid. It is a crucial component that determines the valve’s performance and resistance to abrasion and corrosion.
A pinch valve is a type of control valve that uses a pinching effect to regulate fluid or gas flow. In contrast, a solenoid valve is operated electronically, using a solenoid to open and close tubes for controlling the flow of liquids or gases.
A pinch valve features a pinch tube to regulate the flow, while a plug valve is a quarter-turn valve primarily used for shut-off applications. The historical origins of the two valves also differ, with the Romans introducing the first plug valves to control water pipelines. Click here for the detailed comparison.
Diaphragm valves are a comparable alternative to pinch valves. Both types of valves have a similar function and design, with a soft seal rubber element fitted in the valve housing to stop the flow of media.
A pinch tube is a flexible tube (rubber sleeve) that is pinched to control the flow of a substance. It is a key component of a pinch valve, as the tube is pinched to control the flow of liquids or gases through the valve.
Another name for a pinch valve is a squeeze valve. This name reflects the mechanism by which the valve controls flow by squeezing a flexible tube or sleeve.
Yes, a pinch valve can regulate flow by controlling the opening and closing of the flexible tube or sleeve. This mechanism allows for precise control and adjustment of the flow of liquids or gases through the valve.
Yes, it operates in a linear manner. The valve’s control mechanism allows for proportional and consistent regulation of flow, making it suitable for various flow control applications.
The maximum operating pressure of a manual and control pinch valve is dependent on the type and nominal size, and typically ranges between 3 and 40 Bar. This pressure range allows for versatile applications in different industries and systems.
Advantages of Using Pinch Valves
Minimal Maintenance Requirements
Pinch valves are advantageous due to their minimal maintenance requirements, making them a cost-effective choice for various applications. With their simple yet robust design, these valves eliminate the need for frequent maintenance interventions, helping to reduce downtime and operational costs. By requiring minimal servicing and upkeep, they offer a practical solution for industries seeking efficiency and reliability in their fluid control systems.
Enhanced Control Over Media Flow
Pinch/squeeze valves provide enhanced control over media flow, allowing precise regulation of liquid or gas movement. The valve’s flexible elastomer sleeve effectively throttles the flow, enabling operators to manage the rate and volume of the conveyed substance with precision. This level of control is particularly beneficial in applications where accurate flow regulation is critical, such as in wastewater treatment, pharmaceutical production, and chemical processing.
Resistance to Corrosion and Abrasion
Another key advantage of using pinch (squeeze) valves is their inherent resistance to corrosion and abrasion. The elastomer sleeve acts as a protective barrier, shielding the valve body from corrosive materials and abrasive media. This resistance ensures the longevity and durability of the valve, even when handling aggressive substances. It also makes these valves a reliable choice for demanding environments where other valve types may succumb to wear and degradation over time.
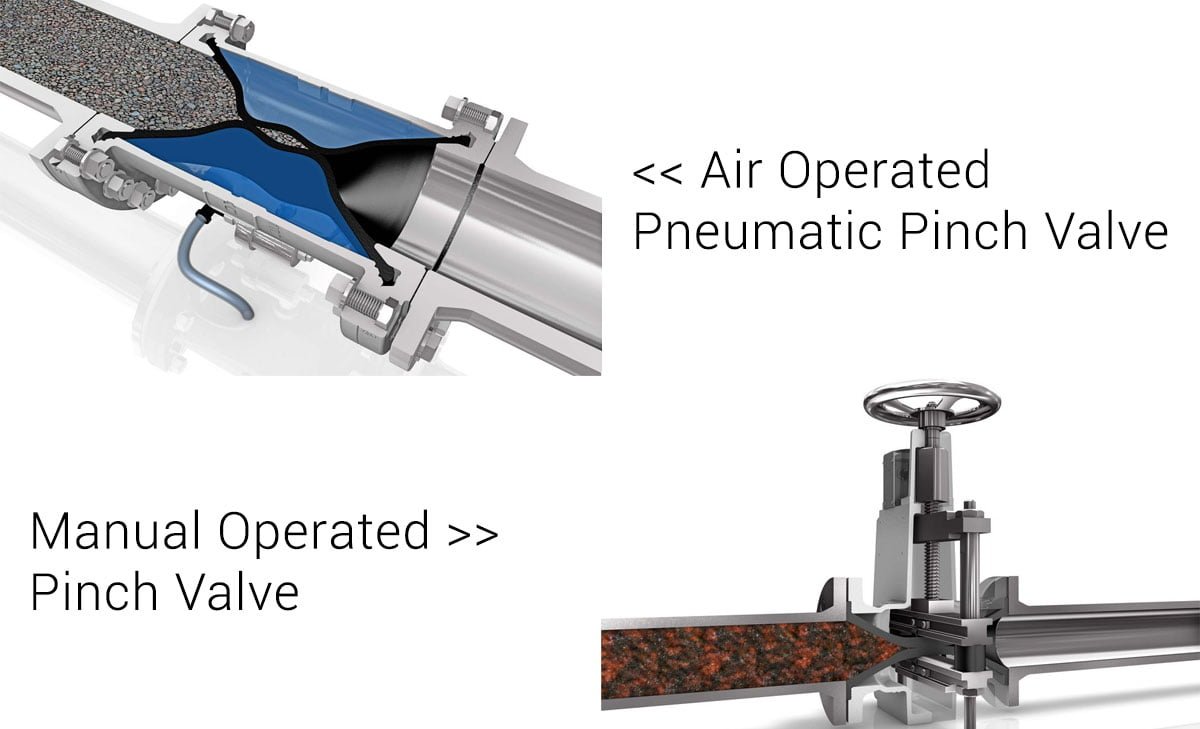
Image Credit: AKO ARMATUREN GMBH
Potential Disadvantages of Pinch Valves
Limitations in Operating Temperatures
Pinch valves are prone to limitations in operating temperatures, which can impact their performance in certain industrial settings. Extreme temperatures, whether high or low, can affect the flexibility and integrity of the elastomer sleeve, leading to potential malfunction or reduced lifespan of the valve. High temperatures may cause the sleeve to degrade or lose its elasticity, while low temperatures can cause the sleeve to stiffen, increasing the risk of cracking or tearing.
These limitations necessitate careful consideration of the environmental conditions in which the squeeze (pinch) valve will be employed, as well as the selection of suitable sleeve materials to withstand the specific temperature range.
Wear and Tear of the Sleeve Component
Another potential disadvantage of pinch/squeeze valves is the wear and tear of the sleeve component over time. In applications where the valve is frequently actuated or encounters abrasive media, the elastomer sleeve may experience accelerated wear, leading to the need for more frequent maintenance and replacement. This can result in increased downtime and operational costs for the system.
Additionally, the gradual deterioration of the sleeve material can compromise the sealing and throttling capabilities of the valve, affecting its overall reliability and efficiency. Proper monitoring of the sleeve condition and proactive maintenance practices are essential to mitigate the impact of wear and tear on the performance of valves.
Selecting the Right Pinch/Squeeze Valve
Understanding Flow Requirements
Pinch (squeeze) valves are suitable for a wide range of applications, but selecting the right one involves understanding the specific flow requirements of the system. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, and temperature fluctuations need to be carefully considered to ensure that the chosen valve can effectively handle the flow demands without compromising performance or safety.
Assessing Valve Size and Connection Type
When selecting a pinch/squeeze valve, assessing the valve size and connection type is crucial. The size of the valve should align with the flow requirements and the overall system capacity. Additionally, the connection type must be compatible with the existing piping infrastructure to facilitate seamless integration and operational efficiency. Consideration of factors such as pipe diameter and connection methods is essential in this assessment.
Considering the Media’s Chemical Compatibility
Pinch valve selection also involves considering the chemical compatibility of the media that will be flowing through the valve. Understanding the properties of the media in terms of viscosity, corrosiveness, and composition is critical in choosing the right valve that can withstand the specific chemical environment without degradation or contamination. Compatibility with the media ensures the longevity and reliability of the valve in its intended application.
Operating Parameters for Pinch Valves
Pressure Considerations
Operating parameters for pinch valves are crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Pressure considerations play a significant role in the functioning of these valves. It is essential to assess the pressure ratings and ensure that the valve is capable of withstanding the specific pressure levels within the system. These valves are designed to accommodate varying pressure ranges, and understanding the pressure requirements of the application is imperative for effective operation.
Temperature Ranges for Optimal Performance
In addition to pressure considerations, the temperature ranges for optimal performance are key operating parameters for pinch valves. These valves are engineered to function within specific temperature limits, and it is essential to adhere to these parameters for reliable operation. Operating these valves within the recommended temperature ranges ensures efficient performance and prolongs the lifespan of the valve components.
Adjusting for Flow Velocity and Solids Content
When considering the operating parameters for pinch valves, adjusting for flow velocity and solids content is essential. The flow velocity within the system impacts the valve’s operation, and it is important to calibrate the valve to accommodate varying flow rates effectively. Moreover, accounting for solids content in the media flowing through the valve is crucial for preventing potential blockages and ensuring smooth operation.

Image Credit: Met-Chem, Inc.
Comparison: Pinch Valve vs Plug Valve
Pinch valves and plug valves are both essential components in industrial piping systems, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these two types of valves can help in selecting the most suitable option for specific operational requirements.
1. Design and Operation
Pinch Valve
Utilizes a pinching mechanism to control the flow of materials through a flexible pinch tube. The valve is actuated by either manual or automatic means, allowing for precise regulation of flow rates. This design makes pinch valves particularly well-suited for handling slurries, solid materials, and dense fluids.
Plug Valve
A quarter-turn valve that features a cylindrical or tapered plug to control the flow of fluid. By rotating the plug within the valve body, the flow can be smoothly shut off or allowed to pass through with minimal obstruction. Plug valves are commonly used for on/off applications in various industries.
2. Material Compatibility
Pinch Valve
Due to its flexible pinch tube design, pinch (squeeze) valves are capable of handling abrasive and corrosive materials without compromising performance. This makes them a preferred choice in applications where material compatibility is a critical factor.
Plug Valve
Plug valves are available in a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, cast iron, and various alloys, offering compatibility with different types of fluids and gases. This versatility makes plug valves suitable for diverse industrial environments.
3. Flow Control Capabilities
Pinch Valve
The inherent ability of pinch/squeeze valves to regulate the flow of viscous and abrasive media makes them ideal for applications requiring precise control over material transfer and processing. The pinch tube design also minimizes the risk of clogging, ensuring reliable operation.
Plug Valve
With its quarter-turn operation, plug valves are well-suited for quick and efficient shut-off of flow. While they may not offer the same level of precision in flow control as pinch/squeeze valves, plug valves excel in providing reliable sealing and low torque operation.
Maintenance and Durability
Pinch Valve
Typically requires minimal maintenance due to the absence of internal parts that come into contact with the media, making it suitable for handling abrasive and corrosive materials.
Plug Valve
Generally requires regular maintenance due to the wear and tear on the plug and sealing surfaces, particularly in applications with high flow velocities and abrasive media.
Pressure and Temperature Handling
Pinch Valve
Capable of handling high-pressure applications and can effectively operate within a wide range of temperatures, making it versatile for various industrial environments.
Plug Valve
Suitable for moderate to high-pressure applications and exhibits good performance across a broad temperature range, making it adaptable for diverse process conditions.
Application Considerations
Pinch Valve
Ideal for applications involving slurries, wastewater treatment, mining, and chemical processing where the handling of abrasive and corrosive materials is common.
Plug Valve
Commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and petrochemicals, where frequent operation and reliable shut-off capabilities are required.
Comparison: Pinch Valve vs Diaphragm Valve
Pinch valves and diaphragm valves are both crucial components in various industrial applications, and understanding their differences and best use cases is essential for optimizing processes. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision.
1. Design and Operation
Pinch Valve
Utilizes a flexible elastomer tube, which is pinched to control the flow of media, making it suitable for handling slurries, liquids with large solids, and abrasive fluids.
Diaphragm Valve
Employs a flexible diaphragm to regulate flow, making it ideal for controlling clean, corrosive, and viscous fluids with precision.
2. Material Compatibility
Pinch Valve
Compatible with a wide range of media, including slurries, powders, and liquids with suspended solids, due to the minimal contact between the valve and the media.
Diaphragm Valve
Suited for applications involving sanitary or sterile processes, as it offers high purity and minimal dead space.
3. Flow Control Capabilities
Pinch Valve
Offers excellent throttling capabilities with minimal pressure drop, making it suitable for applications requiring precise flow control.
Diaphragm Valve
Provides fine control over flow rates and is often used in applications where accuracy is critical.
4. Maintenance and Durability
Pinch Valve
Known for its simple design and ease of maintenance, making it a cost-effective option for handling challenging media.
Diaphragm Valve
Requires periodic maintenance to ensure the diaphragm’s integrity, especially when handling aggressive or abrasive fluids.
5. Pressure and Temperature Handling
Pinch Valve
Capable of handling high-pressure and high-temperature applications, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Diaphragm Valve
Designed to withstand moderate pressure and temperature ranges, making it suitable for general industrial processes.
6. Application Considerations
Pinch Valve
Ideal for applications in mining, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing industries where robustness and versatility are crucial.
Diaphragm Valve
Commonly used in pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and biotechnology industries where sanitary and precise fluid control is paramount.
Conclusion
In summary, pinch valves are an essential component in numerous industrial applications, providing a reliable and effective method for controlling the flow of abrasive, corrosive, or granular materials. By utilizing a flexible tube that can be pinched to regulate the flow of powders or liquids, these valves offer a simple yet efficient solution for fluid control, while minimizing the risk of contamination.
Despite their advantages, it’s important to consider the operating parameters, selection criteria, and potential drawbacks when incorporating pinch valves into a system to ensure optimal performance and longevity.