Demystifying Solenoid Valves: A Technical Breakdown

Introduction
The solenoid valve, an often misunderstood yet essential part of many mechanical and electronic systems, can be somewhat of a mystery to those unfamiliar with it. But don’t let the jargon and technical terminology deter you; once you get to know them, you’ll see that solenoid valves are incredibly useful and versatile devices.
What is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device engineered to manage the flow of fluids or gases. The operation of the valve is influenced by an electrical current, which is channeled through a solenoid. The solenoid, made up of a coiled wire, triggers a magnetic field once it’s subjected to electricity. The engendered magnetic field actuates a plunger housed within the valve, enabling the valve to either open or shut. Consequently, the medium’s flow is governed. Therefore, this valve plays a crucial role in determining if a system will allow or inhibit the passage of fluids or gases.
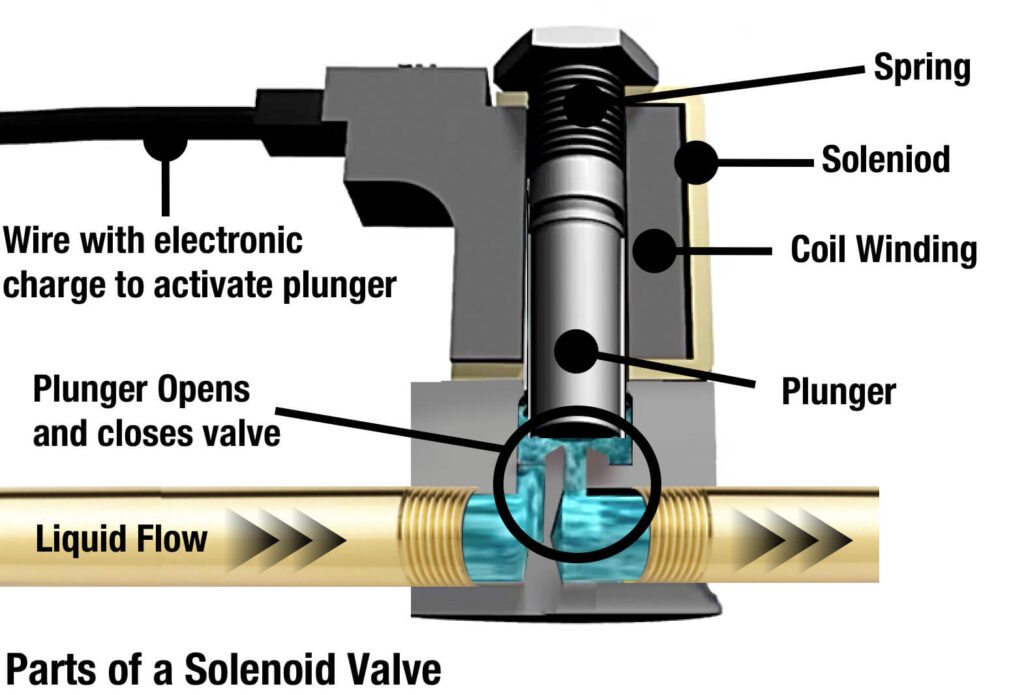
Image Credit: SafeRack.com
Components and Structure of a Solenoid Valve
A solenoid valve is constructed with a number of key components that contribute to its function. Central to these components is the solenoid coil, a helix-shaped wire that initiates the creation of a magnetic field when an electric current is channeled through it.
Situated inside the solenoid coil, we find the plunger. This piece, typically made of iron, is magnetically susceptible and thus is drawn toward the generated magnetic field. The movement of the plunger is what leads to the opening and closing mechanism of the valve.
Encompassing these elements is the valve body. This is the channel where the fluid or gas intended for control is housed. Depending on the type of solenoid valve, the valve body will possess one or more orifices which facilitate the passage of the medium.
The interplay between these three primary components—solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body—is what enables the valve to function as a control device. The solenoid coil generates a magnetic field upon electrical stimulation, which in turn moves the plunger. This movement then alters the state of the valve—either opening or closing it—thereby controlling the flow of the medium contained within the valve body.
Thus, by understanding the role and interaction of these components, we can gain a deeper insight into the workings of a solenoid control valve.
Types of Solenoid Valves
Understanding the diversity of them can help to discern their application in different settings.
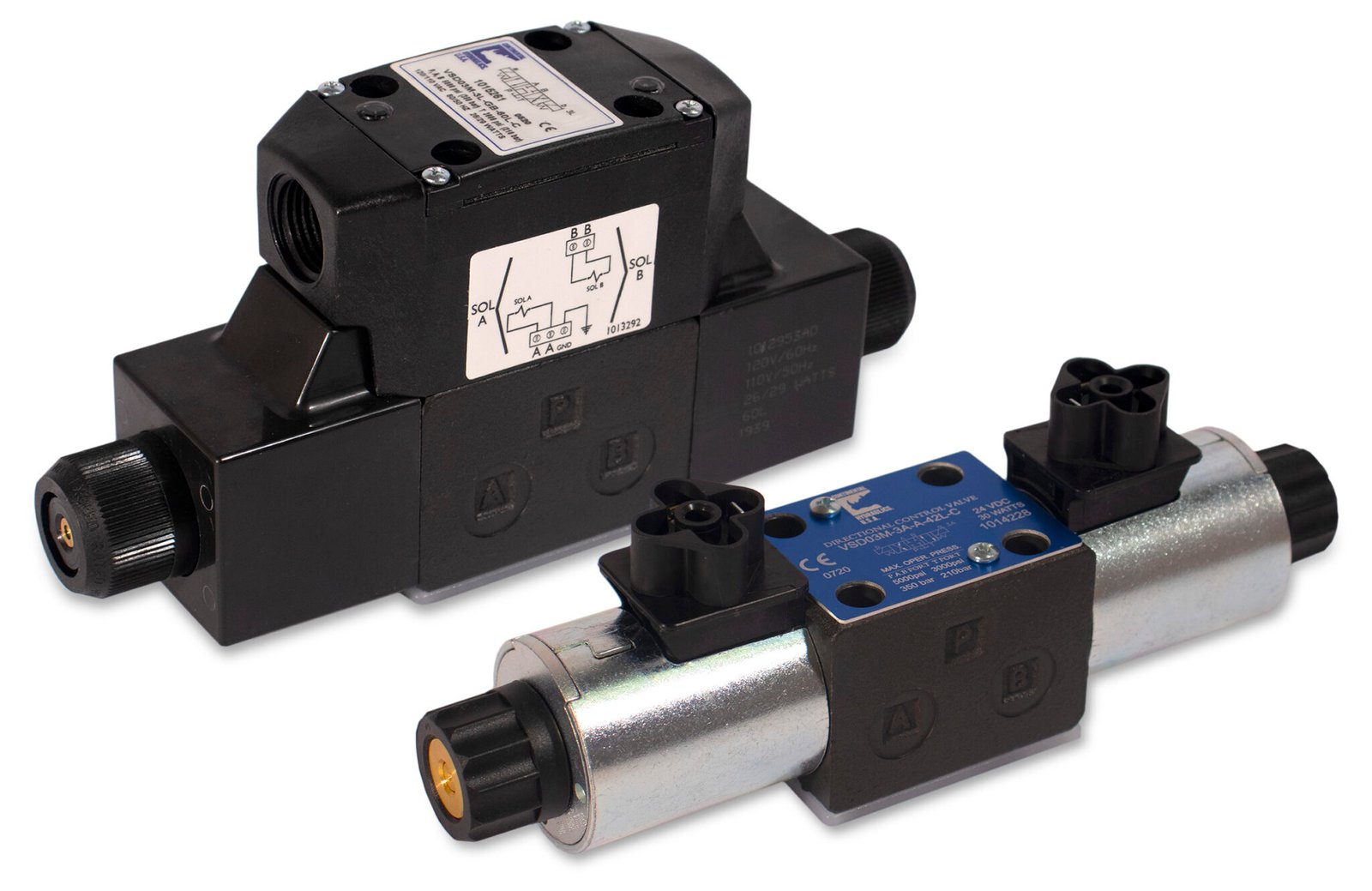

Image Credit: CONTINENTAL HYDRAULICS
Hydraulic Solenoid Valve
A hydraulic solenoid valve plays a crucial role in hydraulic systems by regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid. They rely on a solenoid coil that generates a magnetic field, enabling the quick and precise movement of hydraulic fluid, critical for heavy machinery and hydraulic actuators operation.
Its effective operation enables the smooth functioning of numerous hydraulic equipment including excavators and power steering systems, thereby ensuring high-performance and optimal efficiency. This also enhances the overall safety in operations by providing precise control over the flow of hydraulic fluid.

Image Credit: RS Components
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve
Pneumatic solenoid valves are integral to various applications that use compressed air, such as in industrial automation systems. Their operation is based on changes in air pressure, allowing for precise control in shifting, shutting off, or dispensing compressed air. Particularly, they use solenoid—an electromagnetic coil, to modulate the air pressure. Their instant response to the changes in electrical current makes them highly effective in various pneumatic operations.
Purge Solenoid Valve
Purge solenoid valve is a type of solenoid valve that controls the flow and release of gas emissions in a vehicle’s engine. It is an essential component of the car’s emission system that aids in reducing harmful pollutants discharged into the environment.
They are normally found in vehicles that come equipped with an internal combustion engine. By swiftly opening and closing, they ensure that harmful emissions are vented out in a controlled manner, effectively reducing the overall impact on the environment.

Image Credit: Heschen
Water Solenoid Valve
A water solenoid valve is commonly utilized in appliances like dishwashers and washing machines, helping to regulate the flow of water into the machine. With its capacity to instantaneously start and stop water flow, it provides the machine with precise control over its water use, which can significantly impact the appliance’s efficiency and performance. They work on an electrical mechanism that facilitates their ability to react quickly to electrical signals. The key to their functionality lies in the solenoid coil which, when electrified, creates a magnetic field to open or close the valve.
Irrigation Solenoid Valve
The irrigation solenoid valve is used primarily in the agriculture sector, playing a vital role in automatic watering systems by regulating water flow to different areas of a farm or garden. Known for its efficiency and reliability, this valve reduces manual intervention and conserves water by only releasing it where and when necessary. These valves function based on electrical signals, opening and closing to allow or cease the water flow through a magnetic field generated by an electrical current. By utilizing this system, it enables the precise regulation of water for crops and gardens even in the owner’s absence.
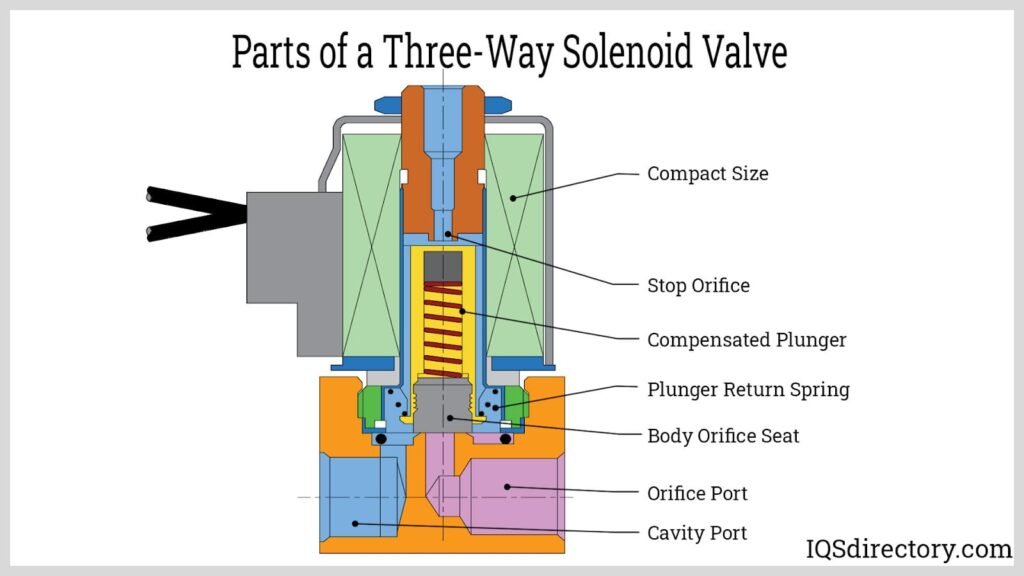
Image Credit: iqsdirectory.com
3-way solenoid valve
3-way solenoid valve is a unique type of valve with three distinct paths or channels for the medium to flow through. This characteristic design allows it to offer more complex and flexible functionality compared to its 2-way counterparts. It has three port connections and two valve positions. It can perform various functions such as stop, distribute, or switch the flow of medium. Typically, in three way solenoid valve, one port serves as an inlet that accepts the medium (such as air or liquid), while the other two ports serve as outlets where the medium exits. This design enables one valve to manage multiple tasks simultaneously, thereby streamlining operations.
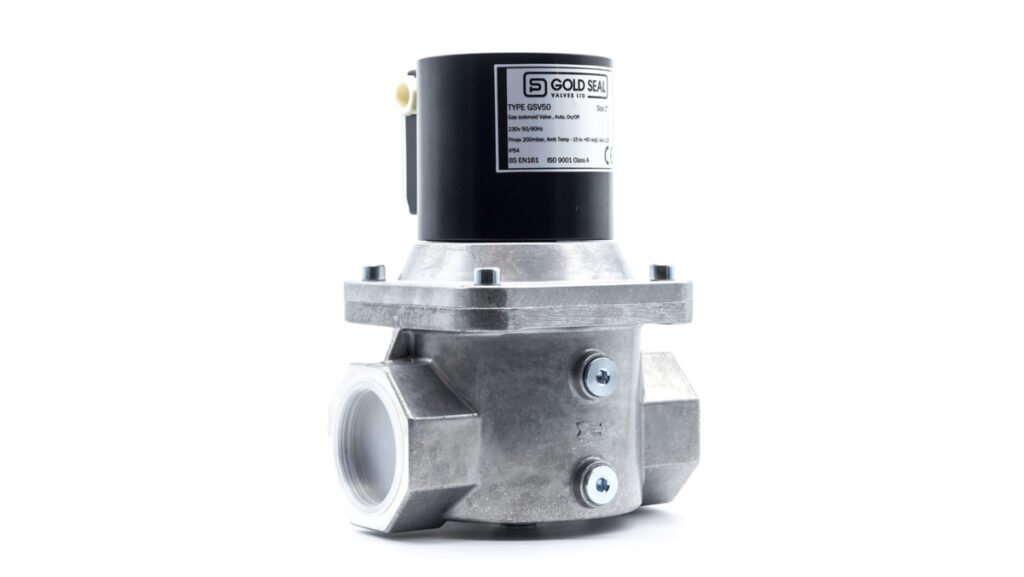

Image Credit: oceaniagassafety.com
Gas Solenoid Valve
Gas solenoid valves are a critical component in gas handling systems, effectively controlling the flow and shut-off of gas in various applications. They function by employing an electromagnetic solenoid to alter the current state of the valve, thereby ensuring a reliable and swift response to gas flow regulation. This helps maintain safety standards in numerous industries, including home appliances, commercial heating and cooling systems, and various manufacturing processes.
Commonly used in kitchen ranges and central heating systems, these valves ensure safety by immediately shutting off the gas flow in case of a detected leakage or malfunction, thereby preventing possible fire hazards. Additionally, they enable precise regulation of gas flow, contributing to improved efficiency and energy savings in different applications.
Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
A direct acting solenoid valve is often found in systems that require fast and immediate response times, such as safety applications. These valves rely on the direct action of the solenoid plunger to open or close the valve, which happens swiftly due to direct electrical input, allowing for instantaneous flow regulation. This capability makes them a crucial component in numerous applications including fuel systems, medical devices, and cooling systems, providing reliable and effective fluid or gas management. With their efficient functionality, they prove essential for systems requiring swift reactions and absolute reliability.
Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve
A pilot operated solenoid valve functions differently than a direct acting valve. It uses a solenoid to control a small pilot valve, which then regulates the larger primary valve. This process enables greater flow rates and the handling of high-pressure applications, making them ideal for industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and power generation. Unlike the direct-acting valve, pilot operated valves can be configured in either normally open or normally closed states depending on system requirements. Their robust design and reliable operation also enable them to withstand challenging environmental conditions.
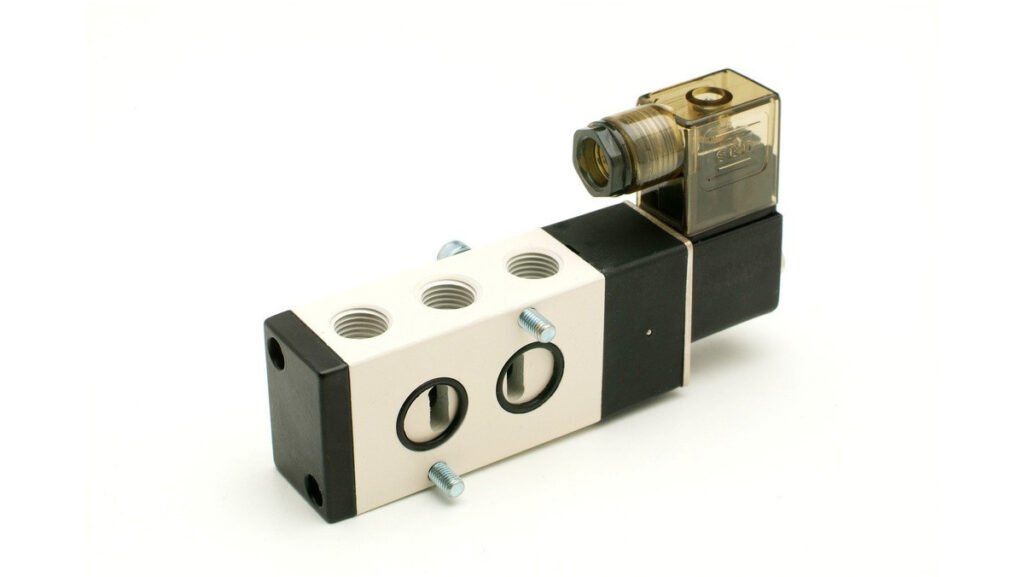

Image Credit: valvesonline.com.au
NAMUR Mount Solenoid Valve
In other words, this breakdown provides a basic understanding of different types of solenoid valves, highlighting their functionalities, applications, and the role of solenoid in their operation. Simply put, these valves serve different roles in controlling fluid or gas flow in various sectors from hydraulic systems to emission control in vehicles and even in household appliances. Indeed, these intricate devices play a fundamental part in our daily lives without us even realizing it, and their effectiveness, adaptability and reliability make them invaluable across numerous industries. With the right type of valve chosen for a specific application, a higher degree of control, safety and efficiency can be achieved.
How Does a Solenoid Valve Work?
The functioning of a solenoid valve is intrinsically tied to its core components, notably the solenoid coil, the plunger, and the valve body. Typically, in a dormant state, a resilient spring secures the plunger, ensuring the valve stays closed. Upon energization, the solenoid coil springs into action, yielding a magnetic field. This magnetic attraction draws the plunger upward, leading to the opening of the valve, thus permitting the controlled medium—be it fluid or gas—to traverse through.
Conversely, when the coil’s electric supply is cut off, the magnetic field ceases to exist, allowing the spring to reassert its hold on the plunger. This forceful action pushes the plunger back to its original position, thereby sealing off the valve. This process epitomizes the simplistic yet effective control mechanism underpinning the operation of a valve.
In the context of more intricate valve configurations, such as the pilot operated or 3-way solenoid valves, the functioning mechanism involves added layers of complexity. Despite these differences, the fundamental principle of electromagnetic force driving a plunger to regulate flow remains the same. It’s this combination of mechanical and electrical elements that gives the valve its unique utility and widespread applicability in various fields.
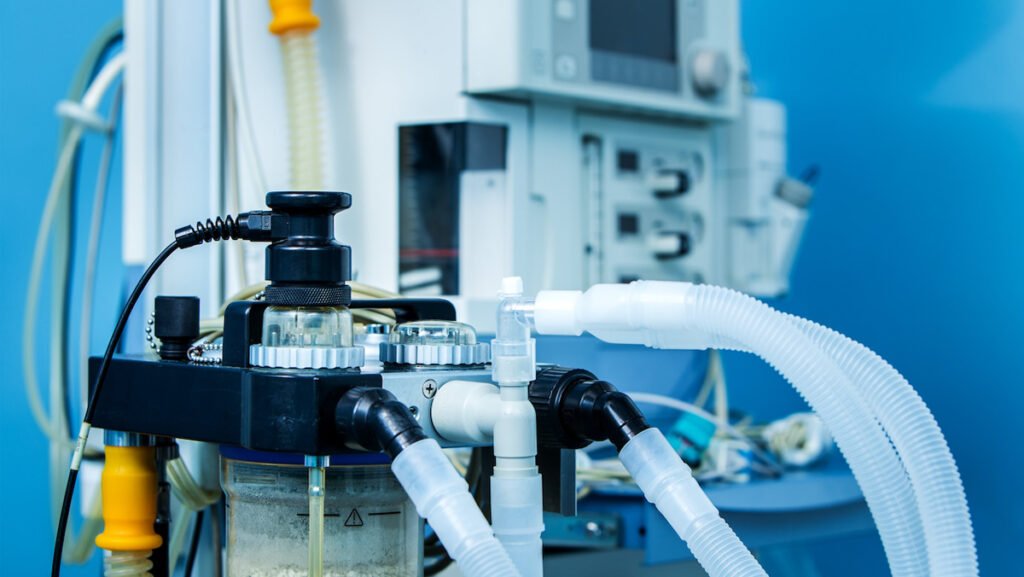

Image Credit: beadelectronics.com
Applications of Solenoid Valves
The versatility and reliable operation of solenoid valves have made them indispensable in a myriad of industries and applications. Residential appliances such as dishwashers and washing machines employ these valves to precisely manage the flow of water. In automotive systems, they are integral in controlling processes such as fuel injection and automatic transmissions, offering quick response times and fluid management.
In the industrial sector, solenoid control valves have a broad spectrum of applications. Fluid control systems rely on them to regulate the flow and direction of fluids, offering a high level of precision and consistency. Pneumatic systems often utilize the NAMUR mount solenoid valve for efficient integration with pneumatic actuators, streamlining operational efficiency. In the realm of process automation, the ability of these valves to offer instant and precise response to electrical signals makes them a preferred choice.
From heating and cooling systems, where they aid in the regulation of refrigerant flow, to medical equipment where they control the supply of oxygen or other medicinal gases, the utility of solenoid control valves is vast and varied. Even in our everyday life, from automatic hand sanitizers to drinking fountains, solenoid valves are silently working in the background, facilitating our comfort and convenience.
This wide range of applications not only highlights the adaptability of solenoid valves but also underscores their significance in facilitating controlled and efficient operations across various sectors. Each application leverages the unique properties of solenoid valves, from the simplicity of the direct acting solenoid valve to the complex versatility of the 3-way solenoid valve. By understanding the role of these valves in different settings, we can appreciate the pervasive influence of this humble yet powerful device in our everyday life and beyond.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Solenoid Valves
Ensuring the optimal functioning of solenoid valves demands regular maintenance and occasional troubleshooting. During routine maintenance, the valve body should be cleaned to remove any accumulated debris or residue that could hamper the flow of the medium.
The solenoid coil warrants careful inspection for any visible damage or wear. Over time, the coil may suffer from burnout, a common issue that can result from prolonged exposure to electrical currents. This can be diagnosed by examining the coil for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration or a burnt smell. In such cases, replacing the coil is usually the most viable solution.
A defective plunger may also affect the operation of the solenoid valve. A worn-out plunger may not respond appropriately to the magnetic field generated by the solenoid, thereby compromising the valve’s ability to open or close effectively. Replacing the plunger can help alleviate this issue and restore the valve’s functionality.
Leakage is another common problem that can affect solenoid valves. This can occur due to worn-out seals or incorrect valve installation. If leakage is observed, it’s imperative to first verify the integrity of the valve’s seals. If the seals are in good condition, checking the installation and positioning of the valve could resolve the leakage problem.
While these valves are generally sturdy devices, addressing these issues promptly is essential to maintain the overall efficiency and longevity of the valve. Remember to always de-energize the valve and follow safety precautions during maintenance and troubleshooting tasks.
This technical yet pragmatic approach to maintaining and troubleshooting solenoid valves ensures they continue to serve their purpose in controlling the flow of fluids or gases in various applications.
Safety and Precautions
When dealing with solenoid valves, adherence to safety protocols is paramount. Start by making sure the valve is fully de-energized before commencing any maintenance, troubleshooting, or handling. This step is crucial in averting any potential electric shock or unwanted activation of the valve. Further, always use the valve within its specified parameters—including voltage, pressure, and temperature ranges. Failure to do so may not only damage the valve but could also lead to hazardous situations.
Equally important is the adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions, which usually contain vital information regarding the installation, operation, and maintenance of the valve. This includes guidance on dealing with specific valve types like direct acting solenoid valve, pilot operated solenoid valve, 3-way solenoid valve, or NAMUR mount solenoid valve. These instructions help ensure the longevity of the valve and maintain its performance efficiency, all while promoting safety.
In conclusion, while these valves are robust and essential devices in many systems, they must be handled with appropriate care and precaution. This approach ensures that they continue to operate safely and effectively, thereby guaranteeing their critical role in controlling the flow of fluids and gases in various applications.

Image Credit: kingsupply.com
FAQ
Are there any safety risks associated with working with solenoid valves, and how can they be mitigated?
Yes, although rare, potential risks can occur due to improper installation, leakage, or malfunctioning of the solenoid valves. These can be mitigated by following manufacturer’s guidelines, regular inspection, and maintenance procedures. For instance, one may ensure the valve is installed properly by cross-referencing with the user manual, preventing the risk of improper installation. Similarly, periodic leak tests can identify and rectify any leaks before they become a significant issue. It is also beneficial to utilize protective measures such as using thermal overload protection in the case of overheating. Trained professionals should also handle any repairs or replacements, to ensure the correct procedures are followed and risk is minimized.
What factors can cause a solenoid valve to fail, and how can they be prevented?
Factors such as extreme temperatures, fluid contamination, and electrical issues can lead to a solenoid valve failure. Regular monitoring and preventive maintenance, including periodic cleaning and electrical checkups, can help prevent such failures. For example, routine inspection of the valve’s wiring can identify early signs of corrosion or fraying, enabling timely repairs to prevent a potential electrical malfunction. Similarly, ensuring the purity of the fluid flowing through the valve can prevent clogs or other forms of contamination-induced failure.
How can I determine the appropriate size and type of solenoid valve for my application?
Determining the right size and type of solenoid valve for your specific application depends largely on factors like the nature of fluid or gas being controlled, the pressure, temperature and flow rate, as well as your system’s electrical requirements. Consultation with a valve specialist or technical expert can be instrumental in making the most appropriate selection. For example, if you’re managing a high-pressure system that involves steam, a direct-acting solenoid valve may be most suitable. However, it’s best to discuss your specific operational parameters with an expert for a customized solution.
Can a solenoid valve be repaired, or is it typically replaced when it malfunctions?
Yes, in many cases, solenoid valves can be repaired by replacing the solenoid coil or the valve’s diaphragm, for instance. However, in cases of significant wear or irreparable damage, replacement of the entire valve might be more cost-effective and efficient. It’s crucial to understand that the lifespan of a solenoid valve largely depends on its working conditions and the care taken during installation and maintenance. Therefore, investing in high-quality components and routine checkups can ensure a longer service life, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
For example, if you have a solenoid control valve installed in an industrial refrigeration system, it may be worthwhile to invest in a higher-end valve designed for low-temperature applications and commit to a schedule of quarterly inspections to monitor for potential issues. This proactive approach could potentially prolong the life of the valve by several years, significantly reducing operational costs. ,
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the mechanics, types, and applications of solenoid valves, such as the direct acting solenoid valve, pilot operated solenoid valve, 3-way solenoid valve, or the NAMUR mount solenoid valve, demystifies their function and potential uses. The simplicity of these components, when combined, form a critical mechanism that facilitates control over the flow of fluids and gases across an array of industries and applications.
Routine maintenance and the observance of safety precautions further ensure their longevity and effective performance. This guide has aimed to provide a comprehensive introduction to the world of solenoid valves, hopefully illuminating their crucial role in our day-to-day life and beyond. The complexities of these robust devices should now be somewhat less daunting, offering insights into their varied applications and the vital role they play in efficient and controlled operation across diverse sectors.