Understanding Plunger Valves: A Beginner’s Guide
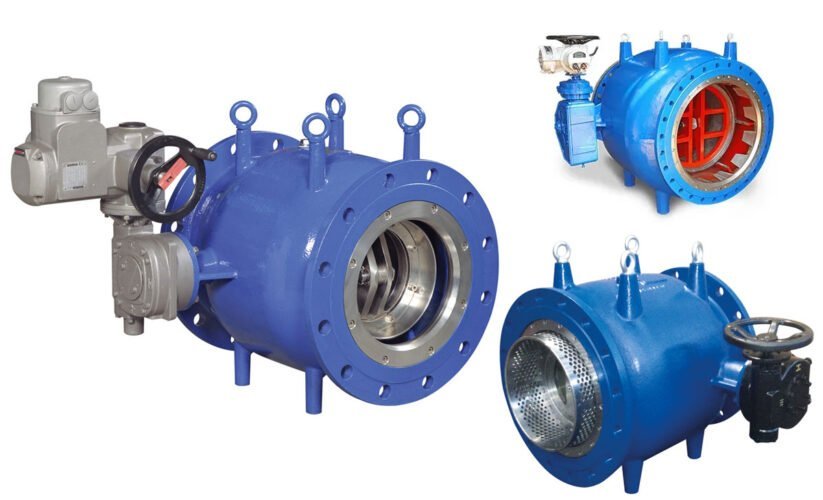

Table of Contents
ToggleThe Comprehensive Guide to Plunger Valves: Types, Usage, Pros, Cons, and FAQs
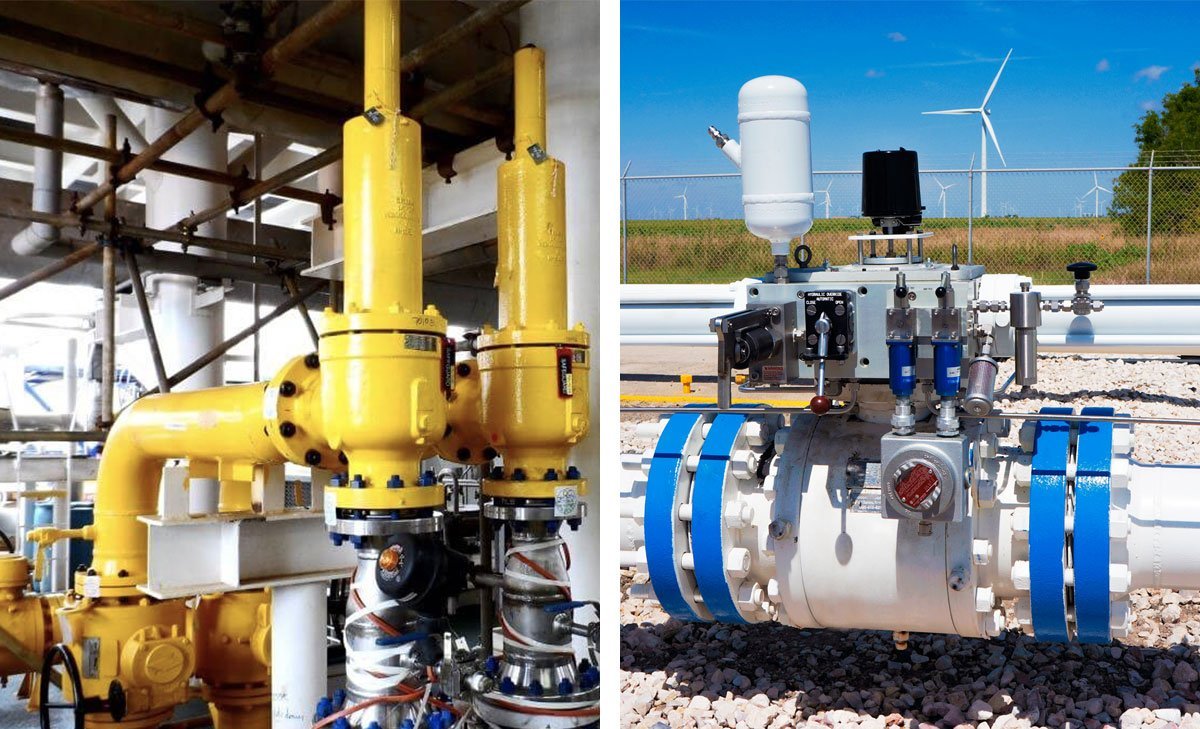
When it comes to controlling the flow of fluids in industrial settings, plunger valves are a crucial component. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of plunger valves, their usage areas, as well as their pros and cons. Whether you’re considering using plunger valves for various applications or simply want to understand their functionality, this guide will provide you with valuable insights. From handling high flow rates to their suitability for fluids with particulates, we’ll cover it all.
Abstract – What is a Plunger Valve?
- Plunger valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of liquid or gas in a system.
- It consists of a cylindrical or conical plunger that can be raised or lowered to open or close the valve.
- The plunger is typically actuated by a manual lever, cam, or solenoid.
- Plunger valves are commonly used in applications where a tight shutoff is required, such as in hydraulic systems, water treatment plants, and industrial processes.
- They are known for their simple design, reliability, and ability to handle high-pressure and high-temperature fluids.
- The sealing mechanism of the plunger valve ensures minimal leakage when closed, making it suitable for critical applications.
- Maintenance of plunger valves usually involves inspecting and replacing the seals and ensuring smooth operation of the plunger mechanism.
- Proper installation and periodic maintenance are essential for the efficient and long-term operation of plunger valves.
Understanding Plunger Valves
Plunger valves are integral components in various industries, serving a vital function in controlling the flow of liquids or gases.
Understanding the basic definition and historical development of plunger valves provides insight into their significance in modern applications.
Definition and Basic Function
Plunger valves operate through the movement of a plunger or piston to regulate the flow of fluid within a system. This mechanism allows for precise control over the volume and pressure of the substance being transported. The plunger is sealed within a cylindrical housing, ensuring efficient fluid flow management.
The basic function of a plunger valve involves the upward or downward movement of the plunger, which opens or closes the passageway for the fluid or gas to travel through. This action enables the adjustment of flow rates, making plunger valves suitable for diverse industrial settings where accurate control is essential.
Historical Development of Plunger Valves
The development of plunger valves dates back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary versions were used to regulate the flow of water for irrigation and domestic purposes. Over time, advancements in metallurgy and engineering led to the refinement of these valves, making them pivotal components in industrial machinery and infrastructure.
During the industrial revolution, the demand for more complex and reliable valves grew, prompting the evolution of plunger valves into precision-engineered devices capable of withstanding high pressures and varying flow conditions. This historical progression underscores the enduring relevance of these valves in modern engineering and manufacturing processes.
Parts of Plunger Valves
Plunger valves consist of several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring efficient and reliable valve operation. From body materials to seals and fasteners, every part contributes to the overall functionality of the valve.
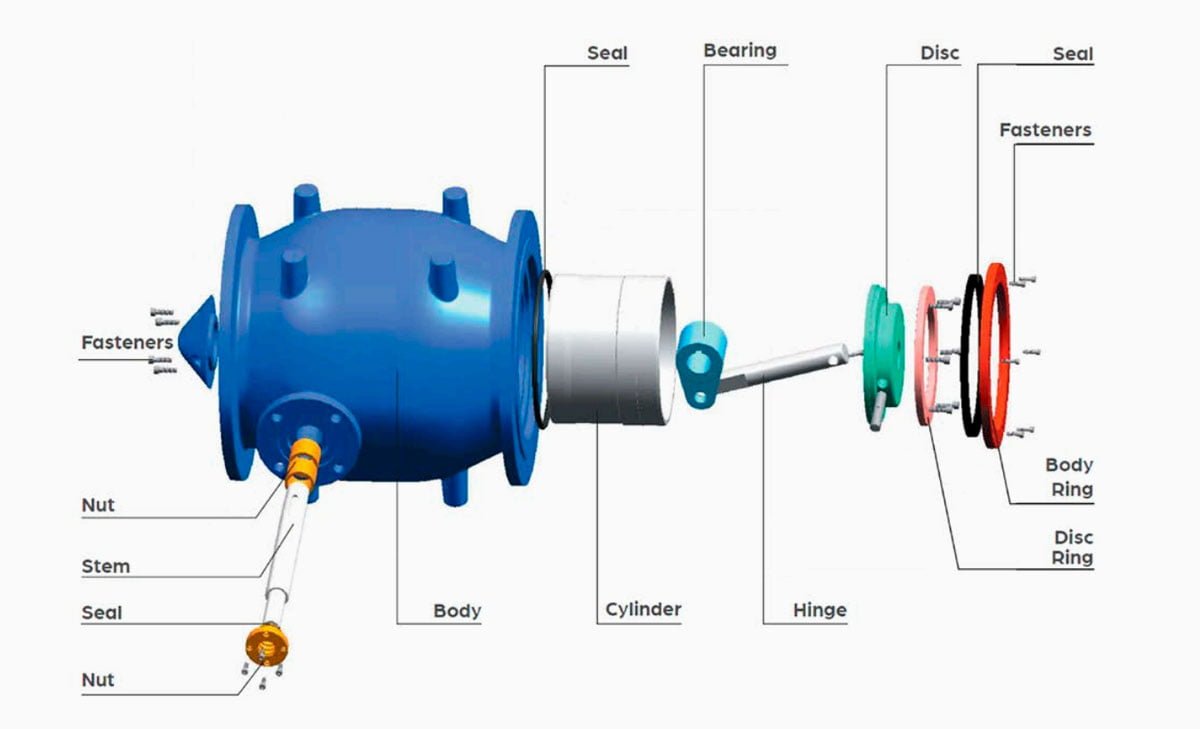
- Body: The body of a plunger valve is typically made of ductile iron or carbon steel, providing the necessary strength and durability to withstand the pressures and demands of fluid control applications.
- Disc: Plunger valves feature a disc, which is available in SS304 or SS316 stainless steel variants. The disc serves to regulate the flow of fluid through the valve, offering resistance and control as needed based on the operational requirements.
- Bearing: SS304 or SS316 stainless steel bearings are utilized in plunger valves to reduce friction and facilitate smooth movement of the valve components, ensuring ease of operation and longevity.
- Hinge: The hinge of a plunger valve, typically constructed from SS304 or SS316 stainless steel, allows for controlled movement of the disc, enabling precise modulation of fluid flow in the system.
- Cylinder: Plunger valves incorporate cylinders made of SS304 or SS316 stainless steel, providing a robust housing for the internal components and contributing to the overall structural integrity of the valve.
- Rings: SS304 or SS316 stainless steel rings are utilized in plunger valves to enhance sealing and prevent leakage, maintaining the integrity of the fluid control process.
- Stem: Plunger valve stems are available in X20Cr13, SS304, or SS316 variants, serving as the conduit for transmitting the actuating force to the disc, enabling precise control over the flow of fluids.
- Nuts: Nuts used in plunger valves are crafted from bronze, brass, SS304, or SS316, providing secure fastening and ensuring the structural stability of the valve assembly.
- Seals: Plunger valves are equipped with seals made of EPDM or NBR materials, essential for preventing fluid leakage and maintaining the integrity of the sealing system within the valve.
- Fasteners: Various types of fasteners are employed in plunger valves to secure the different components and ensure the overall structural stability and reliability of the valve assembly.
With the knowledge of the materials and functions of each component, maintenance, repair, and optimization of plunger valves can be carried out effectively, ensuring seamless operation and longevity in diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Types of Plunger Valves
Manual Plunger Valves
Manual plunger valves are operated by hand, allowing precise control over the flow of liquids or gases. The user manually adjusts the plunger to regulate the flow, making them suitable for applications where a hands-on approach is preferred.
Hydraulic Plunger Valves
Hydraulic plunger valves use hydraulic pressure to control the flow of fluids. They are commonly employed in heavy-duty industrial settings where a reliable and robust valve mechanism is required to manage high-pressure fluid systems.
Pneumatic Plunger Valves
Pneumatic plunger valves utilize compressed air to actuate the plunger, enabling efficient and rapid fluid flow regulation. These valves are often favored in settings where quick response times and minimal maintenance are essential.
Electric Plunger Valves
Electric plunger valves are controlled by an electric actuator, offering precise and automated flow control. They are widely used in automated industrial processes and systems that require consistent and accurate fluid management.
By understanding the distinct characteristics of each type of plunger valve, users can select the most suitable option for their specific application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Common Uses for Plunger Valves
Water Treatment Plants
Plunger valves play a crucial role in water treatment plants by regulating the flow of liquids and gases. These valves are employed in various processes such as filtration, chemical treatment, and disinfection, ensuring precise control over the movement of fluids within the facility. Additionally, plunger valves allow for efficient maintenance and repair of equipment, contributing to the smooth operation of water treatment systems.
Industrial Manufacturing Processes
In industrial manufacturing, plunger valves are utilized to manage the flow of different substances ranging from liquids to granular materials. These valves provide precise control, enabling manufacturers to optimize production processes while maintaining consistent product quality. Whether it’s controlling the flow of raw materials or regulating the release of finished products, plunger valves are essential components in diverse industrial settings.
Residential Plumbing Systems
Plunger valves are integral to residential plumbing systems, controlling the flow of water within homes. From regulating water supply to specific areas of the house to managing drainage and sewage systems, these valves ensure efficient and reliable operation. Their ability to stop, start, or divert the flow of water makes them indispensable in maintaining functional and safe plumbing infrastructures for households.
Agricultural Irrigation Systems
In agricultural irrigation, plunger valves are utilized to manage water distribution, ensuring optimal supply to fields and crops. These valves enable farmers to regulate irrigation schedules, control water pressure, and prevent water wastage. By effectively directing the flow of water, plunger valves contribute to the efficient use of resources in agricultural operations, ultimately supporting crop growth and yield.
Plunger valves serve diverse purposes across different sectors, embodying versatility and reliability in facilitating fluid control and management. Whether in water treatment, manufacturing, residential settings, or agriculture, these valves play a vital role in maintaining operational efficiency and resource optimization.
Advantages of Plunger Valves
Plunger valves, also known as needle valves, offer various advantages in flow control and regulation. Their precision, durability, low maintenance requirements, and versatile applications make them essential components in numerous industries.
Precise Flow Control
Plunger valves enable engineers to finely control and regulate water flow and pressure. The valve’s design allows for precise adjustments, making them suitable for applications where accurate flow control is crucial. Whether it’s in water treatment, power plants, or industrial processes, the ability to achieve precise flow regulation is a key advantage of plunger valves.
Durability and Longevity
Plunger valves are known for their durability and longevity. Constructed to withstand high pressures and varying flow conditions, these valves are designed to maintain performance over extended periods. Their robust design ensures reliable operation, making them a preferred choice for demanding industrial environments.
Low Maintenance Requirements
With their robust construction and minimal moving parts, plunger valves exhibit low maintenance requirements. This not only reduces downtime but also cuts operational costs. The simplicity of maintenance makes plunger valves an efficient and cost-effective choice for industries looking to minimize maintenance efforts while ensuring consistent performance.
Versatility in Various Applications
Plunger valves offer versatility in a wide range of applications, including flow control, pressure regulation, pump start, turbine bypass, discharge, and reservoir inlets. Their ability to handle high differential pressures and diverse media makes them suitable for various industrial processes and infrastructure systems. This versatility makes plunger valves adaptable to different operational requirements, enhancing their overall utility.
Limitations and Considerations
Installation Challenges
When considering the use of plunger valves, it’s essential to be aware of the installation challenges that may arise. Proper installation is crucial, and it often requires precise positioning and alignment to ensure optimal performance. Furthermore, accessing and fitting the valve into complex systems or tight spaces can present challenges that require careful handling and expertise.
Potential for Wear and Tear
One important consideration with plunger valves is the potential for wear and tear over time. The repeated movement of the plunger can lead to mechanical stress, which may result in degradation of the valve components. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to monitor for signs of wear and to prevent any potential issues that may arise from prolonged usage.
Compatibility with Different Fluids
Another factor to consider is the compatibility of plunger valves with different fluids. Certain types of fluids may have specific chemical compositions that could potentially react with the materials used in the valve construction. It’s essential to carefully assess the compatibility of the valve with the intended fluid to prevent any adverse reactions that could compromise the functionality and longevity of the valve.
Cost Factors
Cost is a significant consideration when evaluating plunger valves for specific applications. While plunger valves offer precise control and reliability, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs should be carefully weighed against the benefits they provide. Additionally, the cost of replacement parts or specialized servicing should be factored into the overall cost analysis when considering the implementation of plunger valves in a system.
Choosing the Right Plunger Valve
Assessing the Application Requirements
When choosing a plunger valve, it’s crucial to assess the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as the type of fluid being controlled, temperature, pressure, and flow rate. Understanding these elements will help in identifying the most suitable type of plunger valve for the intended use, whether it’s for industrial, commercial, or residential applications.
Material Selection for Different Fluids
The selection of materials for plunger valves should align with the type of fluid being handled. For corrosive fluids, materials such as stainless steel or PVC may be suitable, while for food-grade applications, materials like FDA-approved plastics or stainless steel are preferred. It’s essential to consider the compatibility of the materials with the fluid to ensure durability and safe operation.
Size and Pressure Ratings
Size and pressure ratings play a significant role in the performance of plunger valves. The size of the valve should be chosen based on the pipe size and flow requirements of the system. Additionally, the pressure ratings should be carefully evaluated to ensure that the selected valve can handle the expected operating pressures without compromising safety and efficiency.
Brand and Manufacturer Comparisons
When considering different plunger valve options, it’s important to compare brands and manufacturers. Look for reputable companies known for producing high-quality valves with a track record of reliability. Consider factors such as product warranties, customer support, and industry reputation to make an informed decision.
By carefully evaluating the application requirements, material compatibility, size and pressure ratings, and comparing different brands and manufacturers, you can confidently select the right plunger valve for your specific needs.
Maintenance Tips for Plunger Valves
Routine Inspection and Cleaning
Regular inspection and cleaning are essential for maintaining plunger valves. It is advisable to create a daily checklist that includes all vital components of the pump system. This may be provided by equipment manufacturers on their websites. Components to inspect should include the water supply and pump for leaks, the engine for proper oil level, gas, and air filter, and the drive system for belt tension and pulley system. Testing the system under pressure to check for leaks and ensure proper functionality is also crucial.
Lubrication and Seal Replacement
Pump manufacturers typically recommend changing the oil after the first 50 hours of operation, followed by replacement every 500 hours or three months, depending on which comes sooner. It is important to consider the type of oil needed, as certain oils perform best with specific pumps. Additionally, it is essential to monitor the wear of components such as packings, brass retainers, valves, plungers, and intermediate ring guides. Knowing the estimated lifespan of these components allows for timely replacements to prevent system breakdowns.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
In cases of plunger valve issues, troubleshooting may involve checking for leaks, abnormal pressure, or unusual system vibrations. It is essential to identify the root cause of these issues and address them promptly. Understanding the common failure points of plunger valves, such as seal wear or damaged o-rings, can aid in troubleshooting and resolving issues efficiently.
When to Call a Professional
While routine maintenance tasks can be carried out by operators, certain complex issues may require professional attention. If troubleshooting efforts do not resolve the problem or if there are indications of significant component wear or damage, it is advisable to seek assistance from a professional with expertise in plunger valve maintenance and repair.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Operate a Plunger Valve
To operate a plunger valve, you simply need to apply force to the plunger, which will create a seal to stop or start the flow of liquid or gas. In most cases, turning the handle or knob attached to the plunger will control the movement, allowing for easy adjustment and precise flow regulation.
Signs of a Malfunctioning Plunger Valve
Signs of a malfunctioning plunger valve may include leaks, difficulty in turning the handle or knob, and inconsistent flow control. Additionally, if you notice any unusual noises such as hissing or rattling, it could indicate a problem with the plunger valve. It’s important to address these issues promptly to avoid potential damage to the valve or the system it is regulating.
How to Select the Right Size Plunger Valve
When selecting the right size plunger valve, it’s crucial to consider the flow rate and pressure requirements of the application. Ensure that the valve can handle the volume and pressure of the substance it will be controlling. Additionally, take into account the pipe size and material compatibility to guarantee a proper fit and optimal performance.
Differences Between Plunger Valves and Other Valve Types
Plunger valves are distinct from other valve types such as ball valves or gate valves due to their unique sealing mechanism. Plunger valves use a plunger (piston) to create a seal, whereas ball valves use a rotating ball and gate valves use a sliding gate to control flow. Understanding these differences can help in selecting the most suitable valve type for specific applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plunger valves and needle valves each have their distinct advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for specific applications. Needle valves excel in providing precise flow control for low flow rates and are reliable, albeit at a higher cost. On the other hand, plunger valves are better suited for high flow rates and handling fluids with particulates, although they may offer less precise control and could experience wear-related leaks. When selecting between these valve types, it is crucial to assess the specific requirements of the application to determine the most suitable valve for optimal performance and efficiency.